1 System Overview
The embedded system is a control, monitoring or auxiliary device, machine and equipment running device; it is a combination of software and hardware, which can cover auxiliary devices such as machinery; has a friendly man-machine interface, supports LCD and GPS modules; mainly completes the GPS positioning Signal data, coordinate conversion, electronic map display and other functions. The software design process is shown in Figure 1.
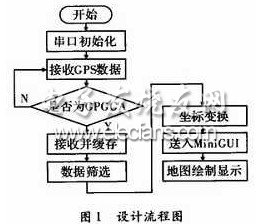
2 Embedded system software design
2.1 Extraction of information output by GPS module
After the GPS module is powered on, it will automatically search for satellite signals and output the calculated data from the serial port. All GPS receivers output data in a universal NMEA format. There are many sentences defined in the NMEA-0183 protocol, but the only commonly used and widely compatible sentences are: GPGGA, GPGSA, GPGSV, GPRMC, GPVTG, GPGLL, etc. as shown in picture 2.

Connect the serial port 0 of the host machine and the development board with a serial port. The host computer enters Linux and opens the Minicom terminal. Set baud rate 115 200, 8-bit data, 1 bit stop, no parity, no flow control. The device file of the serial port is / dev / ttyS *, where ttyS0 is serial port 1, ttyS1 is serial port 2, and so on. Before communicating with the serial port, we must first initialize the serial port parameters and set its properties to ensure that the communication parameters of both parties of the communication remain consistent. After the serial port is initialized, the read operation can be performed. Since the data types sent by GPS all start with the & GPGGA symbol, the & GPGGA symbol is detected, and then the next processing is performed. The key codes are as follows:

2.2 Coordinate transformation
The geographic coordinates output by the GPS module are the WGS-84 coordinate system. The domestic maps are generally projected on the Gauss-Kruger plane based on the 54 Beijing coordinate system. Therefore, it is necessary to make a coordinate conversion, that is, convert GPS coordinates (WGS-84 coordinate system) to electronic map coordinates (54 Beijing coordinate system). The specific steps of coordinate conversion are as follows:
(1) Space rectangular coordinates are converted into national geodetic coordinates, and national geodetic coordinates are converted into map plane coordinates.

(2) Due to the complicated calculation process of x and y, they are not listed here. The results are as follows:

(3) Map plane coordinates are converted into screen coordinates. For example, the scale of the map is 1: k, the length and width of the area to be displayed in the window are M and N, and the pixel points of the window are A & TImes; B, then the positioning data xs, ys coordinates on the window are:

2.3 Electronic map reconstruction
Generally speaking, the data format contained in the electronic map cannot be directly used in the embedded platform, so the data of the electronic map needs to be extracted, stored and reconstructed. At present, the main use is the desktop electronic map system MapInfo, which is the desktop geographic information system software of the American MapInfo company, and has a desktop solution for data visualization and information mapping. MapInfo data format is mainly divided into tab and mif formats. The MIF format is a mechanism provided by MapInfo to exchange data with the outside world. It is mainly used to save the geometric data of spatial objects. After the data of the electronic map is read out, and then under the embedded platform, the electronic map can be reconstituted with a drawing tool. Part of the implementation code is as follows

3 Simulation test
Point test, line test and surface test are shown in Figure 3.

4 Conclusion
Because the system hardware and software platform has a strong upgrade capability, many indicators and functions can be further improved and improved. The conversion from GPS positioning data to electronic map data requires a series of complex algorithms. These algorithms need to be further improved and simplified to improve the system operating efficiency and data accuracy.
Round Smart Watch
Round Smart Watch
everyone enjoys luck , https://www.eeluckwatch.com