The light source is a physics term. Some objects in the universe are luminous, and some are not light. We call objects that we can emit light and are called light sources. The sun, open lights, burning candles, etc. are light sources.
Light sourceThermal effect
The first type is light produced by thermal effects. Sunlight is a good example. Also, candles and other items are the same. Such light changes color with changes in temperature.
Atomic transition
The second kind of atomic transition glows. The fluorescent material applied on the inner wall of the fluorescent tube is excited by electromagnetic wave energy to generate light. In addition, the principle of neon lights is the same. Atomic emission has its own characteristic lines. Scientists often use this principle to identify the types of elements.
Radiation emission
The third category is the light produced by the charged particles inside the material when it accelerates. For example, synchrotron emits synchrotron radiation while carrying powerful energy.
In addition, the pale blue light (the Cherenkov radiation) emitted by the atomic furnace (nuclear reactor) belongs to this category. The so-called "Celenkov radiation" means that the speed of charged particles in the medium may exceed the speed of light in the medium. In this case, radiation will occur, similar to the "sonic explosion."
Note: This is not a true speed of light. The true speed of light exceeds the speed of light in vacuum. This phenomenon is called the Cherenkov effect.

Carbon arc lamp
An electric light source that emits light when the two electric arcs of the contacted carbon rod electrodes are separated after being energized in air. The carbon arc lamp was invented by the British H. David in 1809;
Incandescent
An incandescent lamp, also called a tungsten lamp or a bulb, is an electric light source that heats a filament to an incandescent state and emits visible light using heat radiation. A light source that produces light by heating current through a filament to an incandescent state. It was the earliest electric lamp that was made of heat-resistant glass and contained tungsten wire. Air is drawn from the bulb to prevent the filament from oxidizing or refilling with an inert gas (such as argon) to reduce the evaporation of the tungsten filament by heat. Since only a small portion of the electrical energy consumed by the filament is converted to visible light, the luminous efficiency is low, typically 10 to 15 streams/watt. However, it is easy to manufacture and has low cost.
Low pressure sodium lamp
It is an electric light source that uses low-pressure sodium vapor discharge to emit light. It is coated with an infrared reflective film in its glass housing, which is an electric light source with small light attenuation and highest luminous efficiency. The low-pressure sodium lamp emits monochromatic yellow light, which is used in places where there is no requirement for light color;
HPS
When the lamp starts, an electric arc is generated between the electrodes at both ends of the arc tube. Due to the high temperature of the arc, the liquid sodium mercury vapor in the tube evaporates into mercury vapor and sodium vapor, and the electrons emitted from the cathode collide with the discharge material during the movement to the anode. The atoms of an atom are made to ionize or excite energy, and then return from the excited state to the ground state; or from the ionized state to the excited state, and then return to the base state in an infinite cycle. At this time, the excess energy is released in the form of light radiation. Generated light.
LED lights
LED (Light Emitting Diode), a light emitting diode, is a solid state semiconductor device capable of converting electrical energy into visible light, which can directly convert electricity into light.
The microscope light source in the optical instrument is mainly used to add light to the microscope. It is generally supplied by a voltage of 220V, and the power is generally about several watts. The microscope light source is inlaid with a lamp bead, and the lamp bead is generally an LED lamp. The lamp generates very little heat, so it has little effect on the cooling and heating control of the product at the time of observation. There is also a kind of LED lamp that is not composed of, but composed by the lamp, such a lamp has an external four-plug and built-in four-pin connector. There is also a pair of plugs. Such a light source is only suitable for the light source mounted on the microscope, if it is still relatively dark. There is also a kind of external use, you can freely adjust the lamp, this light is more convenient.

1 light quantity characteristic index. Including the total luminous flux, brightness, light intensity, the amount of ultraviolet light and heat radiation.
2 light color characteristics indicators. Including light color, color temperature, color rendering, color and spectral distribution.
3 electrical specifications. Including power consumption, lamp voltage, lamp current, start-up characteristics and interference noise.
4 mechanical properties. Including geometric size, lamp structure and lamp holder.
5 Economic characteristics. Including luminous efficiency, longevity, price and electricity bills.
6 psychological characteristics. Including lamp appearance and comfort.
Comparison of Luminous Efficiency of Various Light Sources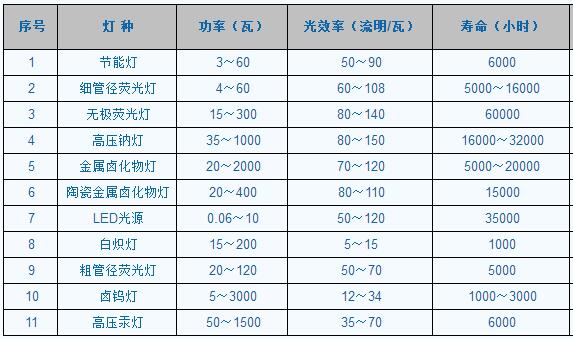
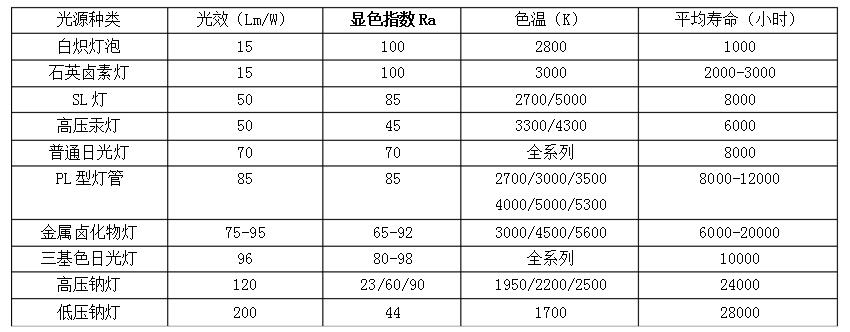
Various light source technical indicators
6.5Inch Coaxial Speaker,6.5 Inch Coaxial,6.5Inch Church Speaker,6.5 Inch Coaxial Speaker
Guangzhou BMY Electronic Limited company , https://www.bmy-speakers.com