[Home Theater Network HDAV.com.cn] Home Theater / HIFI Audio Frequently Asked Questions and Basic Knowledge:
First, the acoustic foundation:
1, noun explanation
(1) Wavelength - the travel of sound waves in one cycle. It is numerically equal to the speed of sound (344 m / s) multiplied by the period, ie λ = CT
(2) Frequency - the number of vibrations per second, in Hertz
(3) Cycle - the time required to complete a vibration
(4) Sound pressure - the physical quantity indicating the strength of the sound, usually in units of Pa
(5) Sound pressure level - Sound power or sound intensity is proportional to the square of the sound pressure, in decibels
(6) Sensitivity - IW noise signal is applied to the speaker, and the sound pressure measured at 1 meter from the sound axis
(7) Impedance characteristic curve - the curve of the impedance value of the speaker voice coil as a function of frequency
(8) Rated impedance - the minimum value initially found after the maximum value on the impedance curve, in ohms
(9) Rated power - an input function that ensures long-term continuous operation without abnormal noise
(10) Music power - the output power (PMPO) calculated from the peak voltage that can be reached instantaneously by the sound signal
(11) Sound Dyeing - The sound is dyed with features that are not available in the program itself, that is, there are more or less components in the reproduced signal.
(12) Frequency response—that is, frequency response. The effective frequency response range is the average sound pressure level in the octave band near the highest peak of the frequency response curve. The average sound pressure level drops by 10 dB, and a line is drawn.
2, question and answer
(1) How is the sound produced?
A: Everything in the world is produced by the vibration of objects in the medium. The speaker vibrates in the air through the diaphragm, which makes the front and rear air form a dense change. This wave phenomenon is called sound wave. The sound wave causes the eardrum to also change densely, and the brain is transmitted, so the sound is heard.
(2) What is resonance? Does the resonance sound have an effect on the sound quality of the Soul Horoscope?
A: If the vibration frequency of an object under vibration is equal to its natural frequency, it is called resonance.
When the object resonates, it does not require a large amount of applied vibration energy to generate a large amount of vibration or even destructive vibration. When the speaker diaphragm vibrates, since the unit is fixed to the casing, the vibration is transmitted to the casing through the basin frame. Partially absorbed, converted into heat and dissipated; part of the wave form re-radiation, because the resonance sound is not the sound of the sound source, it will affect the playback of the speaker, making the sound quality worse, especially the low frequency part
(3) What is the sound absorption coefficient and the sound absorption amount? What is the relationship between them?
Answer: The sound absorption performance is usually indicated by the sound absorption system level “αâ€, that is, α=1-K; the sound absorption amount is expressed by the sound absorption coefficient and the area size of the material. The relationship between the two α = A / S (A is the amount of sound absorption), different materials have different sound absorption coefficients, want to achieve the same amount of sound absorption, is to change its sound absorption area
(4) What are the characteristics of reverberation? What is the difference between reverberation time and delay time?
A: The sound that anyone hears anywhere is a mixture of direct and reflected sounds.
The shuffle has the following characteristics:
There is a time difference between the A direct sound and the reflected sound, and there is also a time difference between the reflected sound and the reflected sound.
The intensity of B direct and reflected sounds, the intensity of reflected and reflected sounds are different
When the sound source disappears, the direct sound disappears first, and the reflected sound continues to propagate back and forth indoors, and does not disappear immediately.
Reverberation time and delay time are two different concepts:
Reverberation time refers to the time required for the indoor reverberation sound energy density to decay to one of its original values ​​of one million (60 decibels) when the sound source stops vibrating. The delay time refers to the time delay of the sound signal, and the sound wave is indoors. Reflection delay forms a reverberation
(5) What is the refraction and diffraction of sound waves?
Answer: The refraction of sound waves is the curve of the sound wave propagation. It is the phenomenon of sound wave bending caused by the change of propagation speed when the sound wave passes through the uneven medium. When a sound wave hits a wall or an object, it propagates along the edge of the object. This phenomenon is called diffraction (also called diffraction). The size of the makeup, obstacle or pore is similar to the wavelength, or the smaller the aperture, the longer the wavelength, the more significant the diffraction phenomenon, so the lower frequency (the lower the frequency, the longer the wavelength), the higher the frequency is more flexible. If the front baffle is wide and the corners are left untreated, severe diffraction can degrade the sound quality.
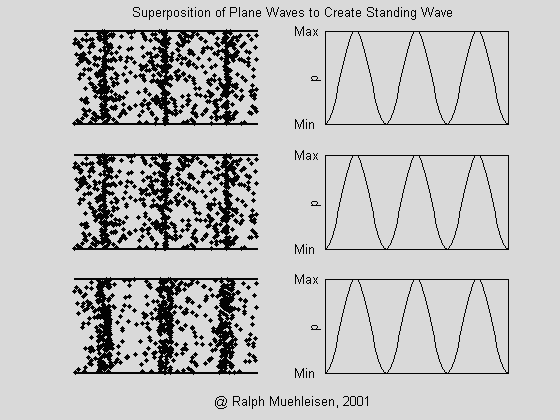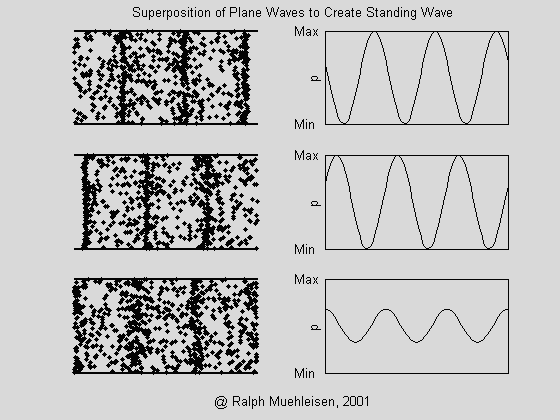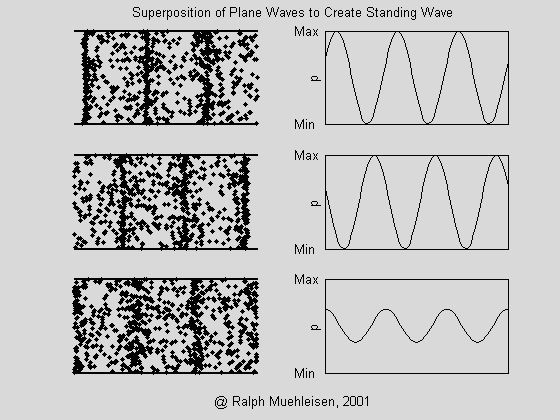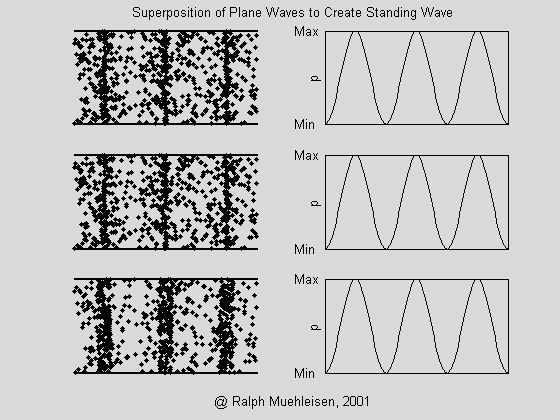
(6) What is standing wave? How does sound wave propagate in the room cause standing waves? Does standing wave vibration make sense?
A: If there are two columns of harmonic harmonics with the same frequency and opposite propagation directions, a standing wave is formed.
For example, several waves in a room acoustic wave exist simultaneously and simultaneously, both incident waves and reflected waves propagating in opposite directions. When the reflected waves are reflected by the incident wave, a standing wave is formed, which causes the propagation medium to vibrate in situ (abdominal point). - Sound waves are strengthened) or not moving (nodes - sound waves are zero).
The auditory sensation of the standing wave is the feeling of the distorted waveform. Just like the power amplifier produces severe nonlinear distortion, it is very poor in listening to the sound inside the room. Once it is difficult to eliminate, when the listener listens to different positions in the indoor station where the standing wave is serious. It will form irregular, uneven high sound level and low sound level at certain frequency points, so that the frequency has "spurt" and "sudden" and the frequency curve is not smooth. Especially for low frequencies below 500 Hz is very significant. Therefore, whether it is indoor space or box design should consider the problem of standing waves, so as not to affect the listening effect.
(7) What is the “sound dye effect� What is its obvious performance? What method is used to overcome it?
A: A single strong reflection superimposed on the direct sound, especially for music, can cause another undesirable effect, called the "staining effect." That is, the signal spectrum has a special change, and the two conditions of the "acoustic dyeing effect" are the delay magnitude and intensity of the reflected sound. For example, as long as a single strong reflection is equivalent to a direct sound delay of no more than 25ms, even if it exceeds several times the direct sound intensity, our hearing is the enhancement of direct sound rather than the acoustic staining effect.
The obvious manifestation of the acoustic dyeing effect: the acoustic feedback phenomenon in the sound reinforcement system.
It is not effective to use a room acoustic equalizer to equalize this peak.
(8) What is the "three elements" of sound?
A: The sound quality is mainly determined by three contents. The pitch, volume, and tone are the “three elements†of the sound. The pitch is changed by the scale and is also the listener's feeling. This feeling is quantified by the frequency of the sound wave: the higher the frequency, the higher the pitch. The volume is the size and strength of the sound. The tone is the harmonic frequency (overtone) component of the diet of the sound.

Second, the speaker base:
1, noun explanation
(1) Bipolar speaker - speaker unit that points to the front and rear of the sound and feeds signals in phase
(2) Dipole speaker - the speaker unit with the sounding unit pointing forward and behind and inverting the signal, the sound radiation pattern is inverted "8"
(3) Subwoofer - a special speaker for ultra-low frequency bands that cannot be reached by ordinary small speakers
(4) Active speakers - components or circuits that amplify audio signals within the speakers
(5) Two-line crossover - a way to transmit the high and low parts of the music signal with two sets of speaker cables
2, question and answer
(1) What is the composition of the speaker?
A: The speaker is mainly composed of three parts:
Enclosure: including empty wooden box, sound absorbing cotton, inverted phase hole, wiring board
Unit: high, medium and low
Divider: If the active speaker includes an amplifier circuit
(2) What is the role of the high, medium and low speaker units?
A: Since the frequency range of the human ear is 20 Hz to 20 kHz, only one speaker unit cannot reproduce the signal of the entire frequency band, so two or more speaker units are used to accomplish this task. If the entire audible frequency segment is divided into three frequency segments of high, medium and low, the corresponding frequency segments are respectively generated by the high, medium and low woofer units.
(3) What is a frequency divider and what is its role?
Answer: The crossover is a kind of circuit safety device built into the speaker. It consists of capacitors, inductors and resistors. Different components form different low-pass, high-pass and band-pass filters. It separates the input music signal into different parts such as treble, midrange, and bass, and then sends them to the corresponding high, medium, and low-range units for playback.
(4) What is a speaker?
A: Any speaker that can convert electrical energy into sound energy is usually called a speaker. Speakers are not only used in civilian and engineering speakers, but also as doorbells, buzzers, etc. There are many types of speakers. According to their transduction principle, they can be divided into: electrostatic (capacitive), pneumatic, electric, piezoelectric, electromagnetic, and ion discharge speakers. Generally, speakers for electric speakers use electric and electrostatic types. The shape of the speaker is: cone, dome shape, horn, plate, and the like.
(5) What is the structure of the speaker?
A: The speakers for general speakers are mostly electric. Taking an electric speaker as an example, the structure is analyzed and composed of three parts: a magnetic circuit part, a vibration part, and a support part.
Magnetic circuit part: upper and lower splint, magnetic steel, magnetic core, (steel bowl)
Vibration part: diaphragm, positioning piece, voice coil, dust cover
Support part: basin frame
(6) What is the role of each part of the speaker?
Answer: The magnetic circuit part: generates a magnetic field. When there is current flowing through the voice coil, the magnetic field line is cut in the magnetic gap. The magnetic class has a strong constant magnetic field to the same sound pressure level, so the vibration amplitude of the diaphragm must be increased, that is, the vibration is increased. The displacement distance of the membrane. Dust and other debris fall into the magnetic gap to avoid noise. The positioning piece ensures that the voice coil vibrates vertically in the magnetic gap of the magnetic steel in the direction of the magnetic core and dampens the free vibration of the diaphragm.
Supporting part: The basin frame mainly connects and fixes the magnetic circuit part and the vibration part.
(7) Classification of speakers:
A: Common speakers can be classified as follows by the same structure and form:
Closed box: air cushion type, ASW type
Inverted box: inverted phase, labyrinth, passive radiation, RI, etc.
Horn speaker: front and rear load
Control directional speakers: spherical, sound column, multi-faceted, etc.
The most commonly used on the market today are closed boxes and inverted boxes.
(8) Can the bookshelf be able to restore the sound effects before recording one to one?
A: It is impossible, it can only be close, not to mention the distortion caused by the speaker, the signal loss caused by the propagation of the wire, and the sound pressure level of 100dB or more easily achieved by the symphony is not achieved by ordinary speakers. What's more, if it is an orchestra, the air volume of the timpani drums will be more than the bookshelf. If you want to produce a near-real stage effect, the bookshelf must have a perfect frequency response and energy reproduction, plus a large enough listening environment.
(9) Is the small speaker more audible than the big speaker?
A: Small speakers have features that are not available in large speakers:
A. The small front panel area makes it easy to create a stage effect in a relatively small listening environment.
B, simple and easy to adjust the crossover network
C, lower cost
However, the well-designed floor-standing speakers have more uniform frequency characteristics and symmetrical high, medium and low-range energy, making the restored audio images more realistic. Therefore, the physical characteristics of the large speakers are significantly better than the small speakers. Under the premise of design, matching and ideal environment, the performance of large speakers is better.
(10) Is the louder the speaker, the better the sound?
A: Not necessarily, the speaker's heavy weight reflects the solid material used in the cabinet and is not easy to cause box vibration, so this is one of the conditions for producing good sound. Many speaker manufacturers use thickened MDF or even high-density boards, or add support bars and sound chambers in the cabinet to reinforce the speaker structure and reduce unnecessary standing waves and sound pressure. Others use metal, concrete, and natural granite to make the box. These can increase the weight of the speaker, so as to prevent the speaker unit from resonating and generating sound and dye during large dynamic vibration. This box sound will greatly affect the sound quality (bass turbidity, midrange cavity).
(11) What is the ABR technology of Zumbo?
A: The adjustable bass reflection structure is referred to as ABR (Adjustabe Bass Reflex), which is used in Jamo's SR170, 200, 300, and 500.
We know that there are bass reflex holes in the phase box. The length of the phase tube is fixed, but the length of the phase tube is adjustable. If the length of the tube changes, the bass volume of the speaker is corresponding. Change, the longer the tube length (clockwise rotation), the stronger the bass, the adjustment range is about +/2.5Db at 100Hz.
(12) Are multiple channels and multiple units worried about the two-way unit?
A: Since the single diaphragm cannot reproduce the full range (20Hz--20KHz), the two-way unit design is a simpler crossover driving method. However, the multiplex design allows each speaker to operate within its optimal frequency response range, covering a wide range, and the frequency response of the entire speaker is extremely balanced and the endurance will be improved. However, every single unit must complicate the frequency divider and the phase is difficult to adjust. Therefore, whether it is multi-channel or two-way design, it has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the environment and actual needs, otherwise it will be a good speaker, but it is not suitable for itself. The professional monitor-grade speakers used in general recording studios are mostly divided by two, mainly occupying a small area, easy to move, and providing relatively accurate tone and analysis.
(13) Is the double wiring column more suitable for single terminal?
A: The double-wired connection speaker reduces the mutual interference between the high, medium and low frequencies. At present, the most thorough approach is bi-amplifier/double-line crossover, but the effect depends on the specific environment. Due to the use of bi-amplifiers, the increase in input power may affect the balance of the entire range. In addition, if the bi-amp/double-line sound is used in a place where the listening environment is small, the original speaker is full and thick, and the sound energy is too much, and the effect is not good.
The true two-line crossover is independent from the binding post to the splitter circuit to the unit, minimizing interference between the unit and the unit. However, some manufacturers only use the two-line crossover terminal, but the internal crossover network is not independent. This fake two-line crossover does not have any effect on improving the sound quality.
(14) What is the function of filling sound-absorbing cotton in the speaker?
A: The attraction material is used to absorb the airflow inside the speaker, reducing the standing wave and resonance. Generally used wool, glass wool, felt, etc., Zunbao's sound-absorbing cotton has a pointed shape, similar to the tip of the anechoic chamber, which is more conducive to attracting standing waves.
For the closed box, since the sound waves behind the speaker are completely absorbed, the sound absorbing cotton generally fills the entire box, which is equivalent to increasing the volume of the box.
For a phase-inverted box, how much sound-absorbing cotton is required depends on the Q value of the different speakers.
(15) Why do civilian speakers use high-pitched treble, while professional products use horns?
A: Because the mid-high and high-range audio sections in the close range are smoother and the sound quality is superior, it is more suitable for home use, so it is mostly used for civilian speakers. The horn-type treble rate is a rising curve, suitable for long-distance listening, otherwise it is easy to make the hearing fatigue. Moreover, the horn-type treble has a wide directivity, and is suitable for theaters and dance halls that are long-distance and require a wide range of directivity.
(16) Why does Jamo use a scaffolding connection in some speaker cabinets?
A: The scaffolding connection means that the components are directly used without using the circuit board.
The method of connecting together. In a general speaker, since the frequency divider is after the power amplifier, the current flowing through the frequency divider is large, and the connection of the copper plate can avoid these disadvantages, improve the conversion efficiency, and improve the sensitivity accordingly.
(17) Does the placement of the speaker have an effect on the sound?
A: Yes. The height of the placement should first be determined by referring to the recommended method in the manufacturer's instructions.
Due to the different acoustic characteristics of each listening environment, the placement of the speakers will have a certain impact on the sound quality.
A The two speakers are too far apart, the middle image is poor, the sound field is hollow, and the sound is scattered.
The B speaker is too close to the back wall and it is not easy to reproduce the original sound field.
The C speaker is closer to the side wall and produces a strong first reflection, reducing the accuracy of the image.
Therefore, due to the environment, the speaker and the original index are quite different, and can be adjusted by the cadence. The general speaker is placed in an equilateral triangle with the listener. If you have spare parts, you can put the speakers in the room one-third of the length of the room, so that you can take good stage sound reproduction.
(18) Is the two 6-inch units equal to the low-frequency energy produced by a 12-inch unit?
A: Not equal. The generation of 2 low frequency response and sound pressure output is calculated based on the volume of air pushed by the unit. If the amount of air pushed by the small unit is the same as that of the large unit, the stroke (displacement of the diaphragm) must be greatly increased, which easily causes intermodulation distortion. And the stroke of the large unit is generally longer than the small unit, so the actual calculation of the amount of air pushed, even 6 6-inch units can not be compared with a 12-inch unit. According to the calculation formula, the low frequency energy produced by two 6-inch units and an 8-inch unit is not comparable.
(19) Is the voice coil of the speaker unit as large as possible?
A: The voice coil diameter of the speaker unit is a factor that affects the high sound pressure value, in addition to the magnetic energy product of the magnetic steel. Different sizes of speaker units have different requirements for the voice coil, and the upper limit can be taken within the specified size range, which results in better frequency response and sensitivity. However, if the diameter obtained is too large, and the magnetic force provided by the magnetic steel is insufficient, it not only increases the cost, but also affects the quality factor of the speaker.
(20) What is the relationship between the speaker and the speaker? Can it be increased or decreased at will?
A: The cymbal of the speaker is related to the woofer used. It is not allowed to increase or decrease at will.
The equivalent 窖 of the speaker is determined by the equivalent vibration radius of the woofer, its resonant frequency and the equivalent vibration quality of the loudspeaker. Therefore, when the speaker is designed, the parameters of the speaker unit can be calculated by testing various parameters of the speaker unit.
(21) The better the frequency response curve of the speaker, the better the sound?
A: The frequency response of the speaker is theoretically a factor that affects the sound quality. Of course, according to other technical indicators, such as sensitivity, harmonic distortion and so on. The most important thing is to listen to the quality and grade of the speaker through the earphones. To give an example: In a speaker evaluation, several experts selected the best speakers through blind listening, and they agreed that a certain speaker system is very good. However, after the actual test in the anechoic chamber, the frequency response curve is very uneven. It can be seen that the frequency is not good and the sound is good.
(22) How to distinguish the frequency response of the standard on the speaker?
A: To distinguish the frequency response, you must know how many ranges of sound pressure levels the target frequency response range changes.
Assume that the frequency domain of the A speaker is 40Hz - 20KHz, but it does not indicate the uniformity of this field. In fact, it has a relatively large loudness attenuation at 60 Hz and 17 kHz, that is, the upper and lower undulations are large in the entire frequency domain. The frequency domain of the B speaker is 50Hz - 19Hz ± 3dB; it is obvious that the frequency response of this speaker is better than that of the A speaker. Therefore, it is necessary to see the error value of the frequency range marked by the speaker.
(23) Why are some speakers' high and midrange units not embedded in the speakers?
Answer: Because the high and midrange units have strong directivity, they will not produce the same sound pressure before and after the diaphragm, as opposed to the woofer. The opposite phase of the sound waves will cause the sound pressure to weaken or cancel each other. Therefore, for high and low sound, the box only has a fixed effect on it. As for whether it is embedded in the speaker, it has nothing to do with the overall situation.
(24) There are many materials for the diaphragm of the speaker unit. Is that good?
A: The top of the dome is divided into a hard dome and a soft dome by material. The former is generally aluminum, titanium, tantalum or ceramics, and its upper limit frequency is higher, but there is an obvious high-frequency resonance peak, and there is an anti-resonance valley in front of the peak. The latter generally uses fabrics or silks such as cloth and chemical fiber. The high frequency upper limit frequency is relatively low, but the curve is flat and the tone is soft and natural.
For the low frequency, the requirements of the diaphragm are light weight and strong rigidity. It should be said that these are two contradictory requirements. In order to find a suitable diaphragm material, the sound workers have made many attempts. Such as the world's magnesium diaphragm, the new 7 series of glass fiber diaphragm, elegant PP diaphragm, Yili aluminum diaphragm, Jinlang sandwich diaphragm, and traditional paper diaphragm.
(25) Why is 20Hz - 20KHz considered to be the ideal speaker reproduction music frequency?
A: The human auditory frequency is generally between 20Hz and 20KHz. If the speaker can replay this band, it is enough. In theory, the frequency of vocal use is between 80 Hz and 1 kHz. The overtone is between 80Hz and 8KHz; the basic frequency of music is 16Hz - 4KHz. These include piano and organ to some metal percussion. The overtone is between 20Hz and 20KHz. The frequency response curve of the general speaker starts to have a large roll-off in the high frequency band of 16KHz, and the human ear feels insufficient about the instrument. Therefore, the high frequency band of the speaker's frequency response is designed to be 30KHz or more, so that there is a good frequency response around 20KHz, so that the human ear hears more overtones.
(26) Some diaphragms have concave or convex corrugations. What is the role?
A: This design is mainly to enhance the internal damping of the diaphragm, so that the frequency curve becomes flatter and more linear, and the sound sounds smooth and smooth. In addition, because the design of the light diaphragm (such as the wire basin) is beneficial to improve the sensitivity, but often the rigidity is not enough, so the wool, carbon fiber, etc. are often added inside the paper cone, so that the diaphragm reduces the split vibration when vibrating. Such a concave or convex waveform advantageously enhances rigidity and reduces distortion of the cone due to severe vibration.

Third, the issue of audio:
1. What is the difference between civilian audio and professional audio?
A: The civilian audio is purely designed for the playback of the home audio system; the professional audio is used for monitoring or sound reinforcement in the studio or performance venue. The characteristics of civil audio: the design is based on the principle of replaying the beautiful sound, paying attention to the details of the sound field, the sound of the instrument, the warm sound effect of the concert hall, etc. The product style reflects the designer's personal hobby. The characteristics of professional audio: the principle of loyalty to the sound, the pursuit of sound quality and accuracy. Professional products are easy to push and dynamic, reliable, and easy to install.
2. What is the basic structure of a standard high-fidelity system?
A: According to this is the signal source (such as LD, CD, DVD), signal cable, preamp, power amplifier, speaker cable, speaker.
3. What is Dolby Surround?
A: A sound that encodes the surround back channel to the stereo channel. A decoder is required to separate the surround signal from the encoded sound during playback.
4. What is Dolby Pro-logic?
A: Added a front center channel to Dolby Surround to lock the dialogue in the movie to the screen.
5. What is Dolby Digital?
A: Also known as AC-3, its digitized audio contains signals for the left front, center, right front, left surround, and right surround 5 channels, all of which are independent full-band signals. There is also a separate subwoofer effect channel. Commonly known as 0.1 channel, together is the so-called 5.1 channel.
6. What is THX and THX5.1?
A: A surround standard developed by Lucas Pictures of the United States, which improves the Dolby Pro Logic Surround system to further enhance the surround sound effect. The THX standard has a strict set of requirements for playback equipment such as audio and video sources, amplifiers, speakers, rooms and even wires. The THX logo is only achieved when the product passed by Lucas. There are two different standards: "The Ultra" and "THX Select", where THX Ultra is the most stringent standard.
7. What is DTS?
A: Short for the separation channel home digital surround sound system. A separate 5.1 channel is also used. Compared with Dolby Digital, the bit rate is higher and the resolution is higher, which is a strong competitor of Dolby Digital.
8. What is DSP technology?
A: DSP is an abbreviation for "digital signal processing." When a dedicated microprocessor handles audio instrumentation in the digital world, it mimics the sound effects that can be found in environments such as concert halls, teaching, jazz nightclubs, and more. DSP technology is also used to decode various environmental acoustic signal forms.
9. What is a D/A converter?
A: A device that converts a digital audio signal (ie, DIGITAL) into an analog audio audio signal (ANALOGUE) in a digital audio product (such as a CD or DVD). The D/A converter can be made as a stand-alone machine, used in conjunction with a CD turntable, which is often referred to as a decoder.
10. What is Bit and Bit Stream?
A: The smallest component of a binary digital signal, which always takes one of two states, 0 or 1. The bit stream is a Philips technology that converts CD digital signals into analog music signals.
11. What is the sampling rate and oversampling?
A: The sampling rate refers to the speed at which the digital recorder or player samples the signal. The sampling rate of CD, DCC and MD is selected as 44.1KHz, that is, 44100 samples per second, DAT is 48KHz or 44.1KHz, digital audio broadcasting. Then use a sampling rate of 32K. The sampling rate determines the highest frequency that the digital system can record. DVD-Audio uses a high sampling rate of 96KHz. Oversampling means that the sampling frequency is several times the standard sampling frequency of the CD system of 44.1 kHz. The purpose is to facilitate the filtering of digital noise after D/A conversion and improve the frequency phase distortion of the CD player. The early CD player used 2 times frequency or 4 times the frequency sampling, the recent machine has reached 8 times or higher.
12. What are the expressions of the sound source in the world?
A: Sound sources can be divided into two categories: analog and digital. The analog type includes an AM/FM radio head, a LP player, a tape deck, a video recorder, etc., and a digital type has a CD player, a LD player, a DVD player, a SACD, a digital broadcast, a VCD machine, and the like.
13. What is the difference between the working principle of Class A, Class B and Class A in the amplifier?
Answer: According to the conduction mode of the power amplifier tube in the power amplifier, there are differences between Class A, Party B and Class A and Class B. Class A, also known as Class A, is a type of amplifier that has a current cut-off in any power output component of the amplifier during the entire period of the signal. Class A amplifiers produce high thermal efficiency when operating, but the inherent advantage is There is no crossover distortion, and single-ended amplifiers are Class A operating methods. Class B, also known as Class B, is a type of amplifier in which the two sets of amplifying elements of the push-pull output stage are amplified and output by the two sets of positive and negative sinusoidal signals. The conduction time of each set of amplifying elements is half a cycle of the signal. Class B amplifiers have the advantage of high efficiency and the disadvantage of crossover distortion. Class A and Class B, also known as Class AB, are defined between Class A and Class B. The turn-on time of each set of amplifying components of push-pull amplification is greater than half a cycle of the signal and less than one cycle. Class A and Class B amplifiers effectively solve the crossover distortion problem of Class B amplifiers, and the efficiency is higher than that of Class A, so it is widely used.
14. What is the difference between a tube amplifier and a transistor amplifier?
A: The tube amplifier is commonly called "amplifier" or "vacuum tube machine", which is used as an amplifying element by the tube; the transistor amplifier is commonly called "stone machine", and the transistor acts as an amplifying element. At the same output power, the tube amplifier has strong overload resistance, and the distortion is small in the case of large signals: since the tube amplifier is isolated by the output transformer, the low frequency response is not as good as the transistor amplifier. The life of the tube is not as good as that of the transistor. Transistor amplifiers can be designed for high power and drive faster than tube amplifiers.
More fresh and fun home theater information, please pay attention to home theater network (WeChat: cnhifi) http://, the country's most influential home theater audio player interactive media website.
The Zipper Earphone is a zippered earphone, belonging to electronic products, including zipper earphone wire, earplugs and plugs, mainly solving the problem that ordinary earphone wires are easily entangled with each other. The earphone cable has a zipper. When the earphone is idle, the earphone cable can be zippered and used to avoid messy and easy to organize the earphone cable. The length of the earphone cable can be adjusted freely during use, and the earphone cable can be restored after being separated. It is very convenient to use in the merged state.
According to the way of changing the earplugs of the Zipper Earphones, there are mainly moving coils and moving irons, and electrostatic and equal magnetic earplugs are relatively few. In terms of wearing form, it is mainly used on the in-ear type and ear-hook type, and the headband type is relatively small. From the earphone wire material, it includes Metal Zipper Earphones, injection zipper earphones, nylon zipper earphones and so on.
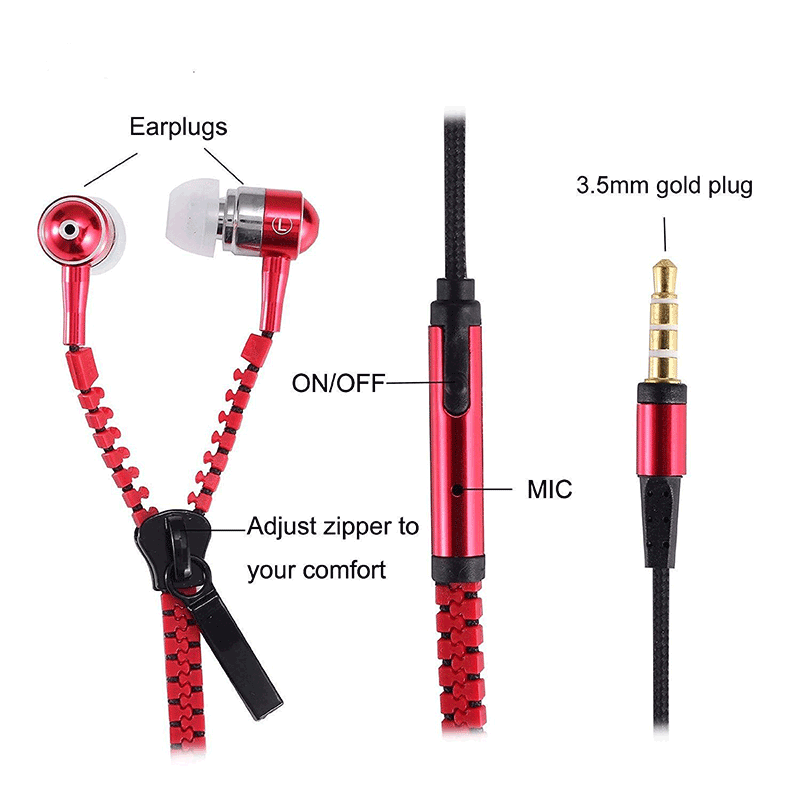

Zipper Earphones
Zipper Earphone,Zipper Headphones,Zip Type Earphones,Pink Zip Earphones
Shenzhen Linx Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.linxheadphone.com