Deep inside the inner ear of a mammal is a natural battery: a small chamber filled with ions that generates voltage to drive nerve signals. According to the physicist organization network recently, researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Hospital and other units have proved for the first time that this "battery" can power implanted electronic devices without harming hearing. Devices implanted into the inner ear can be used to monitor biological activity, such as hearing sounds, imbalances, or response to treatment. Ultimately, the implanted device itself can be developed into a treatment. Related papers were published in the recently published "Nature · Biotechnology" magazine.
"60 years ago we knew there was a 'battery' that was very important for hearing, but no one would use it to power electrical appliances," said Constantia Stankovic, an ear surgeon at the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Hospital.
The ear can convert the mechanical pressure-the vibration of the eardrum-into electrical signals that the brain can process, and the bio-battery is the power source of the signal current. The battery compartment is located in a place called the cochlea in the inner ear, separated by a layer of membrane, where some cells have been specialized into a dedicated ion pump. On the other side of the membrane are unbalanced potassium and sodium ions, combined with the special arrangement of these cell pumps, a voltage is generated. Although the voltage here is the highest in the body (at least for a single cell), it is still very low, and in order not to disturb hearing, the available current can only account for a small part of it.
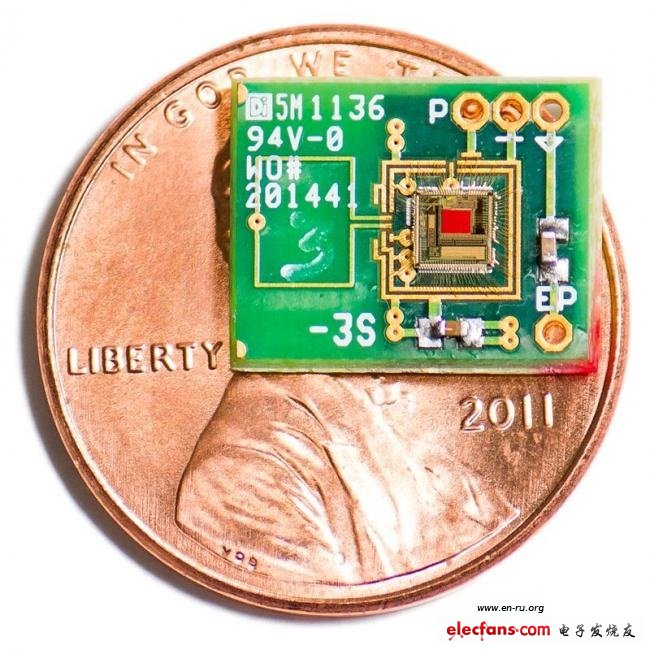
The low-power chip developed by the team of Anasa Chandrakashan, a researcher at the MIT Microsystems Technology Laboratory, solves this problem. They also installed an ultra-low power wireless transmitter on the chip to obtain the detected data. Because the voltage of the bio-battery is unstable, a power conversion circuit is also installed on the chip, just like a box-type converter at both ends of the power line of a general electronic device, which can gradually charge. The charging time is generally 40 seconds to 4 minutes, which can power the transmitter. The signal frequency itself indicates the electrochemical nature of the inner ear.
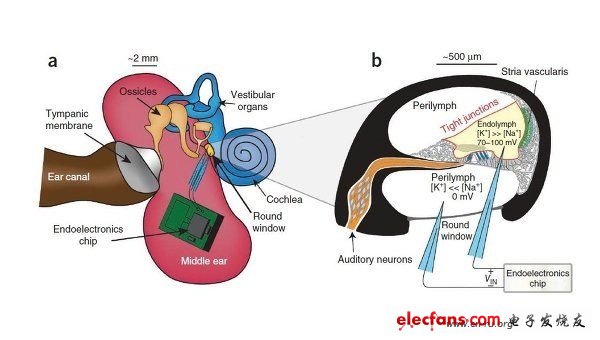
In the experiment, the researchers implanted electrodes on both sides of the guinea pig inner ear biocell membrane, and connected a low-power chip to the electrodes. The chip is left outside the guinea pig, but it is small enough to fit into the middle ear cavity. After implanting the electrode device, the guinea pig responded normally during the hearing test. The device can also transmit data wirelessly and report the chemical conditions of the ear and external receiver.
Cliff Megelion, chairman of the Department of Otolaryngology at Case Western Reserve University, said the study has three possible applications: cochlear implantation, disease diagnosis, and implanted hearing aids. The low voltage of the cochlea itself generates current, which turns it into a power source for powering electronic devices implanted in the cochlea. In addition, if voltages in various disease states can be detected, a diagnostic calculation method may be developed based on this current output deviation.
Packages For Consumer Electronics,Dual Inline Housing,Complex Integrated Circuit,Integrated Circuit Package
Shaanxi Xinlong Metal Electro-mechanical Co., Ltd. , https://www.cnxlalloyproduct.com