Abstract: Different surface treatments will affect the optical and electrical properties of ITO films, and affect the efficiency and lifetime of the entire OLED device. Therefore need to pass the surface properties. This article introduces several commonly used surface treatment methods and compares them.
1 Introduction
Organic light-emitting devices (OLEDs) used in color displays have excellent image quality, especially in terms of brightness and contrast. In the past decade, the research on OLED has received extensive attention, which has brought an incalculable impact on the future image display technology. The performance of the OLED device is very closely related to the hole injection process, by using tin-doped indium oxide (ITO) as the anode of the OLED.
ITO has excellent characteristics such as low resistivity, high visible light rate and high infrared light reflectivity, and has been widely used in solid-state flat panel display devices. The conduction band of ITO is mainly composed of 55 orbits of In and Sn, and the valence band is dominated by 2S orbitals of oxygen. Oxygen vacancies and Sn replace doped atoms, which constitute the donor energy level and affect the carrier concentration in the conduction band. During the ITO deposition process, due to the generation of oxygen vacancies and Sn doping substitutions in the film, a highly degenerate n-type semiconductor is formed. The Fermi level is above the bottom of the conduction band, and therefore has a very high carrier concentration and low resistivity. In addition, ITO has a wide band gap, so the ITO film has a high transmittance for visible light and near infrared light. However, since ITO is a non-stoichiometric compound, the deposition methods, deposition conditions, and surface treatment methods such as spray coating, vacuum evaporation, chemical vapor deposition, reflected ion implantation, and magnetron sputtering will affect the performance of the ITO film, resulting in The work function of ITO surface varies between 4 ~ 5eV. At present, the production of ITO glass has been commercialized. To improve the performance of OLED, the surface of ITO needs to be treated to adapt it to organic thin films.
2 Effect of surface treatment on ITO surface properties
The following discusses the role of ITO surface treatment and its impact on OLED performance from two aspects of electrical and surface properties.
2.1 Effect of surface treatment on ITO surface properties
The ITO anode is the light exit surface of the OLED. The rough ITO surface will diffuse light reflection, reduce the intensity of the emitted light, and reduce the external quantum efficiency of the OLED. The rough ITO surface will affect the internal field distribution of the OLED, and the local high field on the ITO surface will accelerate the aging of organic materials, thereby reducing the life and stability of the device.
2.2 The effect of surface treatment on the electrical properties of ITO
OLED is a hole injection limiting device, and the number of hole injection directly affects the performance of the entire device. By changing the contents of In, O, Sn and C pollutants on the surface, the surface work function can be increased, the barrier for hole injection can be reduced, and the number of hole injections can be increased. ITO is an n-type semiconductor, and electrons are provided by heavily doped Sn4 + and oxygen vacancies. When the content time of these two components on the surface is reduced, the surface work function will decrease.
3 ITO surface treatment method
Commonly used ITO surface treatment methods include mechanical polishing treatment, acid-base treatment, plasma treatment and a combination of the above methods. Before surface treatment, the ITO substrate should be cleaned, followed by ultrasonic cleaning with deionized water, acetone, and anhydrous alcohol for 30 minutes each, and then dried with pure nitrogen. The various surface treatment methods are described in detail below.
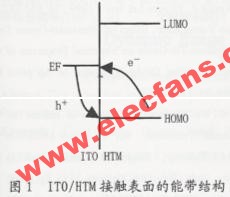
3.1 ITO surface treatment method
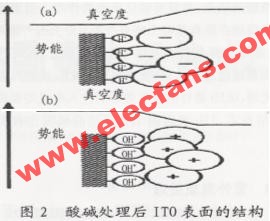
The structure and composition of the solid surface are different from the inside. The atoms or ions on the surface show coordination unsaturation, which is caused by the chemical bonds that are cut off when the solid surface is formed. It is for this reason that the solid surface is very easy to adsorb foreign atoms, causing pollution on the surface. Due to the large amount of water in the ambient air, water is the most common pollutant on solid surfaces. Since the chemical bonds that are cut off on the surface of metal oxides are ionic bonds or strong polar bonds, they are easily combined with highly polar water molecules. Therefore, most clean surfaces of metal oxides are contaminated by water adsorption. In most cases, water finally dissociates and adsorbs on the surface of metal oxides to form OH- and H +, and the adsorption centers are surface metal ions and oxygen ions, respectively.
According to the acid-base theory, M + is the acid center and O- is the base center. At this time, the hydrolysis ion adsorption is performed on a pair of acid-base centers. After dissociating the water on the ITO surface, and then treating the surface of the ITO metal oxide with acid and alkali, H + in the acid and OH- in the alkali are adsorbed by the alkali center and the acid center, respectively, forming a layer of dipole, thus Changed the work function of the ITO surface.
3.2 Plasma treatment
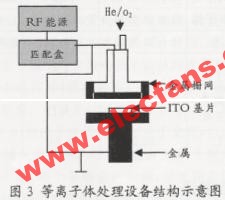
The plasma is usually operated using the equipment shown in FIG. 3. The substrate is placed on the base, different mixed gases are introduced in the vacuum system, and the gas is ionized by a radio frequency voltage on the metal electrode to form a plasma, which bombards the ITO substrate at a very fast speed. In order to form a more uniform electric field, the electrode adopts a metal grid structure. The role of plasma is usually to change the surface roughness and improve the work function. The study found that the effect of plasma on the surface roughness is not large, and can only reduce the root-mean-square roughness of ITO from 1.8nm to 1.6nm, but it has a greater impact on the work function. The methods of using plasma treatment to improve the work function are also different. Oxygen plasma treatment increases the surface oxygen content by supplementing the oxygen vacancies on the ITO surface. Oxygen reacts with surface organic pollutants to form CO2 and H2O, which removes surface organic pollutants. SF6 improves the surface work function by forming a fluorine-containing layer on the ITO surface, and does not change the roughness significantly. Ar plasma treatment is to clean the ITO surface by removing the oxygen absorbed in the process of loading the substrate.
3.3 Mechanical polishing
A large amount of Al2O3 fine powder shot peening flow is sprayed toward the ITO surface at high speed, and the microscopic convex parts of the surface layer are smoothed or flattened by means of its kinetic energy to achieve the purpose of polishing. This method is simple to operate, the surface micro-shape is good, and has no direction. It is mainly used to remove surface area pollution, micro-bumps and shallow lines, and has the effect of strengthening the surface. But the surface roughness can only be improved slightly on the original basis. S. Jung et al. Found that pre-treating ITO by polishing and then annealing can improve the surface roughness and oxygen content. The interface between the organic layer and ITO is smoother, and the luminous efficiency and injection current of OLED devices are increased by about 10 times. The crystallization state of the TPD layer on the ITO surface has also changed.
3.4 UV ozone treatment
Install a low-pressure mercury lamp with a wavelength of 253.7nm in the vacuum chamber. Place the ozone generator and the ultraviolet tube for photolysis ozone in a cylinder with a reflective aluminum film inside to improve the utilization of light energy. When the 3400V high voltage is applied to the metal mesh outside the glass tube of the ozone generator and the two discharge electrodes formed by the inner core of the tube, when the vacuum chamber passes through oxygen, part of the oxygen molecules flowing through the metal mesh are decomposed into oxygen atoms, and are combined with other Oxygen molecules collide to produce ozone molecules. The action of ultraviolet rays directly on the organic matter decomposes the organic matter, which not only forms an oxygen-rich layer on the surface, but also removes carbon pollution on the surface. The comparison of various surface treatment methods is shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Comparison of various surface treatment methods
Surface treatment method | Surface resistance (Ω / □) | Work function (eV) | Surface roughness (nm) |
Unprocessed | 16.1 | 4.5 | 2.6 |
Mechanical polishing | 16.3 | 4.2 | 2.3 |
Ar plasma | 16.7 / 17.3 / 17.0 | 4.5 | 10.9 / 15.4 / 23.0 |
Oxygen plasma | 16.4 / 15.0 / 16.4 | 4.35 / 4.75 / 4.65 | 1.4 / 1.4 / 2.1 |
Wang Shui | 18.5 / 23.5 / 28.6 | 4.6 / 4.3 / 4.7 | 3.8 / 8.4 / 8.8 |
Aqua regia / oxygen plasma | 27.7 | 4.6 | 6.0 |
Oxygen plasma / aqua regia | > 30.0 | 4.7 | 1.8 |
HCL | 26.3 | 4.54 | 1.3 |
4 Conclusion
Through the above comparison, it is found that the mechanical polishing method can obtain the smoothest ITO surface, the oxygen plasma treatment can obtain the highest work function ITO surface, and the UV ozone treatment ITO surface has the lowest resistivity. Only by combining multiple methods can the best performance of ITO surface be obtained.
Ceramic Disc,Ceramic Disk,Ceramic Discs With Holes,Alumina Ceramic Dis
Yixing Guangming Special Ceramics Co.,Ltd , https://www.yxgmtc.com