The NP (Number Portability) service means that the user changes the operator but the subscriber number remains unchanged. China is currently carrying out on-site testing of mobile number portability services in some cities. In order to provide users with better service experience after the number is ported, field trials require that the current interworking and interworking services of the mobile network can also be normally used after the number is carried, including voice services, point-to-point short message services, and point-to-point multimedia. Message business and so on.
After the number is carried, the user's ISDN number cannot represent the network where the user is. Therefore, when the operator network receives a phone call, a short message, or a multimedia message in a local network where the number is carried, it needs to query the number portability database ( NPDB) to determine the called subscriber's current subscription network and route according to the routing number returned by the database.
From the perspective of routing technology for number portability services, there are two levels of technical issues that we need to consider:
Which operator is responsible for querying the number portability database. After the number is carried, a session may pass through at most three carriers' networks, including the originating operator's network where the calling user is located, the receiving operator's network where the called user is located, and possibly the network with the called number. The inter-network routing solution, which operator is responsible for querying the database, is the first issue we need to consider.
How to query the number portability database. What technical solutions need to be adopted when an operator searches the network for a number to carry a database is the second issue that we need to consider.
This article will analyze the advantages and disadvantages of different technical solutions from the above two aspects, combined with the actual situation of China's telecommunications network, and introduce the technical solutions determined by our field tests.
1 Inter-network routing scheme carried by our number1.1 Comparison of Different Route Plans
Internationally, there are usually two types of inter-network routing schemes for number portability. One is the originator's network query database, and the other is a network query database owned by the called number. Route diagrams are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, respectively.
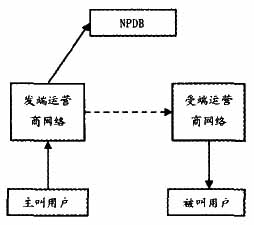
Figure 1 Originating Network Query Database
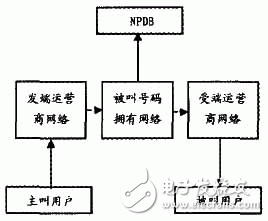
Figure 2 The called number owns the network query data.
Figure 1 shows that the originating network query refers to the carrier's network where the calling user's carrier directly queries the number portability database to obtain the current carrier's information of the called user, and then directly connects the session to the called user's current subscription network. , the receiver carrier network. The receiving carrier's network may belong to the same network as the originating carrier's network, or it may belong to the same network as the called number's owning network, or it may be a third-party carrier's network.
As can be seen from FIG. 2, the called number has a network query, which means that the operator's operator's network follows the original route and connects the session to the called number owning network. After the called number owns the network, it is responsible for querying the number portability database to obtain the information of the current operator of the called user, and then directly connect the session to the current subscription network of the called user, ie, the receiver operator network. The receiving carrier's network may belong to the same network as the originating carrier's network, or it may belong to the same network as the called number's owning network, or it may be a third-party carrier's network. If the called user is a user carrying the originating operator's network, the receiver's operator network and the originating operator's network are the same operator's network, and a route detour occurs.
The advantages and disadvantages of the above two routing schemes have been compared theoretically by many international organizations.
The biggest advantage of the originating network query with respect to the called number having a network query is that it avoids routing detours and wastes network resources. However, this solution also has certain disadvantages. Since all the called numbers (including the local network and other network numbers) need to query the NPDB to determine their subscription network, this method can reduce the signaling if the proportion of the users is high. The number of handovers and connection time are more efficient; conversely, if the proportion of the users is low, this method will cause a large number of invalid queries of the originating network to the NPDB, and thus the efficiency is low.
The called number has a network query scheme applicable to the case where the originating network does not have the capability to initiate an inquiry to the NPDB, including that the originating network is a fixed network (assuming that only mobile number is carried), or that a network other than the carrying area is implemented. If the rate of carrying users is small, this method can reduce the number of queries to the database. However, when the user brings in the originating network, such a scheme will cause a route detour; and when the called user is carried to the third party network, the number owning network also participates in the call transfer process, thus wasting network resources.
During the selection of inter-network routing plans during field trials of mobile number-taking between China's inter-network mobile networks, a comprehensive analysis was made of the inter-network routing conditions of various services in China, the number portability management policies during field trials, and the current network architecture in China. The factors weighed the cost of various operators' transformation and the advantages and disadvantages of various options. Finally, the routing plans for various services during field trials were determined. The following will be analyzed by business category.
1.2 Voice Services Between Mobile Users
For voice services between mobile users, the on-site trial phase determines the use of the originator's network to query the database.
In determining the inter-network routing solution for voice services, China initially held different opinions from operators. Each of them analyzed the network conditions of the operator, the size of the users, and the situation of inter-network calls in the network, and proposed the inter-network routing solutions that were most suitable for the operator.
Currently, there is a large gap in the scale of operators in China. For networks with smaller users, they are more inclined to have a network query for called numbers. This is mainly because if the originating query is used, all inter-network traffic needs to access the database, and for operators with smaller users, the proportion of inter-network traffic to all traffic is very large, so the new database query is added. The volume will be relatively large and the amount of network modification will be relatively large. In particular, for a local network carrying a one-way number portability, only carriers that are allowed to bring in the network are allowed to use. If you use the called number to have a network query plan or you do not even need to build an NPDB, the amount of network modification is relatively small. However, this solution increases the burden on the carrier, wastes the line relay resources, and increases the dialing delay of the call carrying number.
Of course, the advantages of originating network queries are also obvious. It is generally acknowledged that the originating network query can reduce the routing detours, does not involve the number owning the network, does not waste the line relay resources, and does not increase the dialing delay of the call carrying number because of the number portability, and can better guarantee the service quality to the users. Therefore, most countries in the world use this routing method.
Finally, we have taken comprehensive considerations from the entire communications industry in our country and determined the technical solution for using the originating network query. This scheme is very beneficial to the country in the country to carry out number-portability services in the country.
1.3 Voice Services Between Fixed Users and Mobile Users
For voice services between fixed subscribers and mobile subscribers, the on-site trial phase determines that the called number has a network query database.
Earlier we have analyzed the advantages and disadvantages of the two routing schemes. However, due to the fact that only the mobile user's inter-network number is carried during the field trial phase in China, in order not to affect the fixed network, we have determined that the called mobile number should have a network query.
Considering that after the reorganization of telecommunications, all operators in China are full-service operators. In the future, when operators build fixed and mobile integrated gateways, they can gradually change to the method of originating network query. After connecting to the operator's mobile network, after querying the database by the mobile network and continuing the connection, the negative effect of routing roundabout can be reduced.
1.4 Point-to-point short message service
For the point-to-point short message service, the on-site trial phase determines that the called number has a network query database.
At present, the point-to-point short message service in China is not exactly the same as the Lu Nan method of the telephone service. Therefore, when selecting a technical solution, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the actual situation of the short message service. The plan should be considered based on the following status quo:
· At present, the short message service of each operator in China, the short message center is set up in the province as a unit, so the NPDB inquired by the short message center should contain at least NP data of all users in the province.
· The G network does not communicate with each other. That is, the originating subscriber's home message center can send short messages to all users of the local network. CMSC provinces are interconnected between SMSCs, and short messages are sent from the calling subscriber to the short message center to the called subscriber's home short message center, and then the short message is delivered to all local users of the province.
• Internet messaging uses the method of originating and accessing the Internet, that is, direct access to the Internet at the location of the calling user.
Based on the above background, we have conducted a detailed analysis of the amount of network transformation of the two routing schemes of the short message service.
(1) Using Originating Network Query
Because the originating network is required to inquire, the originating short message center (SMSC) needs to query the NPDB where the called number is located for all the messages between the intranets. The network modification requirements are as follows:
· The SMSC of the entire network must be reconstructed. For other network numbers, the process of querying the HER must also be triggered. It cannot be directly transmitted over the network.
• For other network numbers on the other network, the originating SMSC needs to add all GT data of the local network and other network subscriber numbers in the signaling network of the G network in order to be able to query HLRs in different places or to access NPDBs in different places; in the C network signaling network To add all GT data of this site and other users in the province. Or build an NPDB for all SMSC queries in the country. The NPDB needs to store NP user data of all local networks in the country. However, if the proportion of users carrying users is high, the capacity requirement for NPDB will be relatively large.
• For SMSC, Internet Gateway (IWGW), and Signaling Transfer Point (STP): It is required to identify the called number with the Routing Number (RN) prefix.
(2) Use the called number to have a web query
It is only necessary to modify equipment such as SMSC, IWGW, and STP, and it is required to identify the called number with the RN prefix; the called number has the process that the network SMSC needs to trigger access to the HLR for other network numbers, and the other still maintains the existing SMSC. The process of accessing the HLR does not require additional modifications.
It can be seen that, for the short message service, the request for reconstructing the network of the originating network is very complicated. Even if the numbers are carried on only a few local networks, the entire network equipment needs to be reconstructed; and the network with the number is used to query the existing network equipment. The transformation is few and worth recommending. However, the resulting routing roundabout problem cannot be avoided. The complexity of the settlement caused by routing roundabouts also needs to be considered by the regulatory authorities.
It can also be seen that if the number is carried in the country in the future, in fact, the transformation of the voice service has also completed the data configuration of the STP office of the entire network, that is, the GT translation data of all the segments of the other network has been added to the entire network. Therefore, the originator's query can be neglected compared to the called number's increase in the amount of modification by the network query. At that time, we should consider changing the routing scheme of the short message service to the way of originating network query, which can solve the problem of routing roundabout and the settlement problems it brings.
1.5 Point-to-point multimedia message service
In the point-to-point multimedia message service between mobile users, the on-site trial phase has determined the use of the originating operator's network to query the database.
On this issue, all operators in China have consistently chosen the method of originating inquiries from the beginning. This is determined by the service routing of multimedia messages.
For the multimedia message service, the calling side needs to access the ENUM DNS to query the home multimedia message center of the called user, and the ENUM DNS is set centrally throughout the country. Therefore, if you use the originating network query, you only need to modify or create a new network-wide ENUM DNS so that you have NPDB-related functions. In the field test phase, the NPDB only needs to store the NP information of all NP numbers at the test site.
2 Technical solutions for querying databases in China's operator networksCurrently, there are many technical methods for carrying out database query within the operator's network. Internationally accepted solutions are divided into signaling and intelligent networks:
· The intelligent network mode mainly accesses the NPDB through the switching node and completes the translation of numbers. Currently, most mobile MSCs have SSP capabilities. Therefore, the key point for smart network service implementation is that the switch analyzes the number dialed by the user and then goes to the database to query the routing number.
• The signaling method is mainly to query the database and obtain the next routing number in the existing signaling flow. A signalling relay (SRF) functional entity may be added between two SPs (which may be MSC, HLR, SMSC, etc.). The SRF functions connected in series between SPs can usually be implemented in STP, and can also be implemented in separate physical entities.
Taking into account that the access number-bearing database is an action within the operator's network, different operators can adopt different schemes without affecting the communication requirements between the networks. Therefore, at the on-site testing stage, China’s regulations stipulate that all operators can use their own network conditions. Select the technical solution for accessing the database.
By evaluating the network architecture of the local network and minimizing the transformation of existing network equipment and signaling networks, China's operators have basically adopted new HLR equipment, built NPDB in HLR equipment, and used MSC (for voice (Service) and SMSC (Point-to-Point Short Message Service) access to the HLR signalling process to achieve access to the number portability database. From the process of accessing the database, we can understand this scheme selected by China's operators as a special signaling scheme, that is, the functions of the SRF are built into the HLR equipment. The multimedia message service has clearly adopted the process of MMSC accessing the EUNM DNS to query the NPDB. It can also be understood as a special signaling scheme, but the business logic is relatively simple. This article will not focus on analysis, but mainly implement voice for operators in China. The business and short message programs are introduced and analyzed.
2.1 Telephone service
China's operator voice service access NPDB program is as follows: SRF equipment with NPDB function built in the HLR, that is, the existing home network HLR (indicated by 1) upgrade, built-in the network to carry out the user's NPDB; HLR (indicated by 2), built-in his network to carry the user's NPDB. The process of using the MSC to query the HLR triggers the query of the NPDB. If you are called a number owned by the local network and access the HLR (1) according to the route before the NP, you can determine whether the user is carrying it out; if you are called another network number, the MSC needs to directly access the HLR (2) to determine whether the user is carrying. The scheme for the transformation of the network is as follows:
• Upgrade the existing HLR (1) to have NPDB functionality.
· Each local network needs to create a new HLR (2) and have NPDB function;
· Need to modify the logic of HLR (1) and HLR (2) to process the MAP signaling of the route query class. For the case of called other network subscribers, it is required to be able to return the RN+ called party number as the roaming number;
The relevant network element equipment needs to identify the routing code indicating the operator's network. For an inter-network call, the call can be connected to the network according to the indication of the routing code.
Among them, for the upgrade of HLR (1), there are also two implementations. One solution is that, after the users of the local network are brought out, the operator directly modifies the data of the existing network HLR (1) and sets the roaming number of the carrying user as the RN+ called party number. In another solution, the HLR(2) periodically updates the data in the home HLR(1) of the user to ensure that the HLR(1) does not change the existing signaling flow when the user is called. In the case of the implementation of the correct route to take out the user. Obviously, the function of the former scheme HLR(2) equipment is relatively simple and the development period is short. However, every time a user takes the user out, the user data in the HLR (1) needs to be modified. Therefore, it is more suitable for a network with fewer HLR devices on the existing network. The NPDB function of the latter scheme is actually implemented in the HLR (2), and the functions are complicated and the development period is long. HLR(1) only uses the original location update procedure and does not need to modify the existing network HLR(1). Therefore, HLR(1) is more suitable for networks with more HLR equipment on the live network. This is also an important reason why different operators in China currently use different solutions.
2.2 Short Message Service
Similar to the telephone service, the short message service also uses the signaling process of the SMSC to access the HLR in the process of the short message service to trigger the query of the NPDB to obtain the information of the user's current subscription network, and then routes the short message.
The realization of the short message service should be considered based on the transformation of the voice service to the network. Because it has been determined that the short message service adopts the inter-network route of the network query database by the called number, the route from the originating network to the called number owning the network remains unchanged according to the original route plan.
When the SMSC of the called party owns the network accesses the HLR (1), the address of the visited VMSC of the user in the HLR (1) will be directed to the HLR (2) according to the configuration that the voice service has been completed. After the SMSC obtains the VMSC address, it will send the short message to the HLR(2), and the HLR(2) adds RN to the called number and forwards it to other operators through the Internet. It can be seen that in the short message service, the HLR(2) needs to simulate the function of the short message center in addition to the function of the VMSC, and forwards the short message to the Internet. For the bringing in user, the HLR (2) directly returns the real VMSC address of the user and completes the routing of the short message.
3 ConclusionAlthough the implementation of number portability, although there are multiple technical solutions can be achieved, we also found that, from the process of determining field trial technology solutions in China and the testing process, any one solution is not perfect, and the scale and network of operators The architecture, existing service routes, user size, intra-network intra-network traffic ratios, number of open ports, and open policies have a very close relationship. No solution can meet the requirements of all operators at the same time. At present, we can only stand at the perspective of the entire industry, and on the premise that the scope of future number-bearing services in China will not be determined yet, we have tentatively established a pilot phase technology. Program. The scheme we choose is not necessarily the best. Therefore, after the end of field trials in the future, we also need to assess the cost of transformation, complexity of transformation, and user feedback. Based on the actual situation, we will consider the technical plan for carrying out number portability in the future.
Fiber Optic Distribution Box,Fiber Optic Breakout Box,Fibre Optic Breakout Box,Fibre Break Out Box
Cixi Dani Plastic Products Co.,Ltd , https://www.dani-fiber-optic.com