introduction
With the increasing demand for energy saving and emission reduction in the whole society and the rapid development of white LED lighting technology, new lighting sources represented by LED lamps will play an important role in the evolution of modern incandescent lamps, and the development of modern society. Provide a more efficient, energy-saving, environmentally friendly lighting environment and excellent lighting quality.
First of all, as an alternative to incandescent bulbs, LED lamps are more closely related to incandescent lamps because of their different illumination principles, construction methods, and usage characteristics. Therefore, based on the characteristics of incandescent lamps, The requirements for the use of the luminaire as a light source are met, and the precondition for the replacement of the LED lamp is to satisfy the established lighting habits, to exhibit its excellent characteristics and to exert its maximum economic and social benefits. For this reason, according to the characteristics of the LED lamp itself, combined with the specific application, the paper focuses on the light distribution structure of the LED lamp, the heat dissipation structure, the performance characteristics of the driving power supply, and some existing problems. At the same time, an alternative is given. The site environment to be considered in the application, as well as the selection method and technical conditions.
1 LED lamp structure features
The structure of the LED lamp is mainly divided into four major blocks: the structure of the light distribution system, the structure of the heat dissipation system, the drive circuit and the mechanical/protective structure. As a unified whole, they are related to each other and need to be comprehensively considered and coordinated.
1. 1 General characteristics of LED lights
Before talking about the general structure of LED lights, let's first look at the structure of incandescent lamps, as shown in Figure 1.
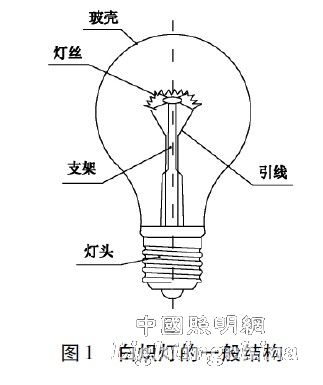
The structure of incandescent lamps mainly includes:
Light distribution system—the filament (light source) is heated to an incandescent state, emitting almost all directions;
The heat dissipation system—mainly radiates heat through the glass bulb;
Drive power source - directly connected to the AC mains power supply, and connected to the filament through the lamp cap and lead wire;
Mechanical / protective structure --- consists of glass bulbs, lamp holders, brackets and other structures.
The structure of the LED lamp is much more complicated than the incandescent bulb, as shown in Figure 2.
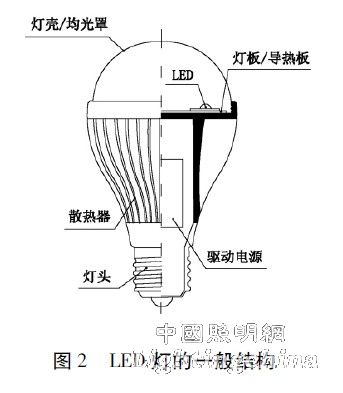
There are:
Light distribution system——— consists of LED light board (light source) / heat conduction board, uniform mask / lamp housing, etc.
The heat dissipation system—is composed of a heat conducting plate (column), internal and external heat sinks, etc.
The driving power source is composed of a high-frequency constant current source and a linear constant current source, and the input is a commercial alternating current;
Mechanical / protective structure --- consists of radiator / casing, lamp / insulation, uniform mask / lamp housing and other structures.
In addition, according to the overall structural characteristics of the two, they can be further divided into:
Incandescent lamp - a single unitary;
LED lights—integrated/split/multi-head combination.