3GPP big secret: how the 5G standard is produced Some people say that 3GPP is a mysterious organization. The world's largest standardization organization has always been known for its rigor and professionalism, but in addition to publishing and developing specifications, the 3GPP standardization body itself is very little known.
Recently, Dr. Chen Wanshi, the chairman of TSG RAN1 who has been working in 3GPP for nearly two months, has done a "Demyst 3GPP" salon in Beijing. For us to unveil the veil of this industry organization.
It is reported that Dr. Chen Wanshi is mainly responsible for the standardization of physical layer air interface (OTA) in 3GPP. He has 17 years of experience in the telecommunications industry. Worked in a number of telecommunications companies. Since joining Qualcomm's R&D team in 2006, he has participated in many technical deployments and standardization work. In August of this year, Dr. Chen Wanshi of Qualcomm defeated another candidate from the election to be the new RAN1 chairman.
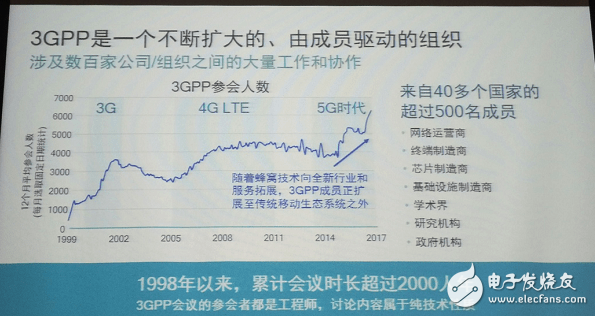
Define a complete end-to-end system specificationPeople who are not in the communications industry may not know much about 3GPP. In fact, even people in the communication circle know little about it. 3GPP is the abbreviation of The 3rd GeneraTIon Partnership Project. It was established in December 1998 and is formed by the cooperation of seven global standards development organizations (SSOs). More than 550 member companies from more than 40 companies Countries. It includes network operators, terminal manufacturers, chip manufacturers, basic manufacturers, and academia, research institutions, and government agencies.

China and 3GPP became attached to China. In June 1999, China Wireless Communication Standards Research Group (CWTS) officially signed in Korea and joined 3GPP. At present, China's three major operators and mainstream communication equipment vendors are members.
With the approach of the 5G era, more and more industries and entities are participating in the 3GPP ecosystem, and the influence of 3GPP is increasing and expanding beyond the traditional mobile field.
The 3GPP specifications and research are jointly promoted by member companies, working groups, and technical specification groups.
It is reported that the original scope of work of 3GPP is to develop global applicable technical specifications and technical reports for the third generation of mobile communication systems. Subsequently, the scope of work of 3GPP has been improved. At present, the projects involved involve cellular telecommunication network technologies, including wireless access, core transmission networks and service capabilities, including codecs, security, quality of service, etc., to provide complete System specification.
For a standardization organization, how many voices can be mastered by the amount of technical specifications in hand. It is reported that at present, 3GPP has 1200 active technical specifications and hundreds of thousands of technical proposals.
The main role of 3GPP is to ensure industry demand, seamless interoperability between different vendors, and provide the global scale necessary for mobile.
Work is a collaborative system level projectUnderstand what kind of company 3GPP is. In the next step, what areas should be covered in the analysis of 3GPP work? How to carry out specifically?
The above mentioned 3GPP working components are three major aspects of RAN, SA and CT. So the main work of 3GPP is to focus on these three aspects. There are also 16 dedicated working groups (WGs) within 3GPP to interface with different projects.

It should be noted that the chairmen and vice-chairmen of these technical specification groups and working groups, all from 3GPP member companies and elected, must be objectively neutral and work on behalf of 3GPP. The technical specification group is elected every two years; it can serve for up to two sessions. Their primary responsibility is to be responsible for the overall management and progress of the work within the group; to manage the meeting schedule based on individual member proposals; to ensure compliance with 3GPP workflows and policies.
The work of 3GPP is a collaborative system-level project that is decentralized. The 3GPP system design work is decided by multiple working groups one by one, with only a small amount of end-to-end supervision. It is managed in a way similar to all other complex system-level projects. For example, a jet plane. This requires that all engineering work depends on the research and development work, technical invention and collaboration of each member.

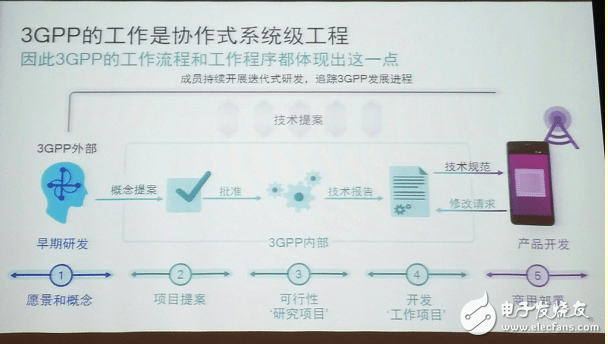
Overall, there are four steps: First, early R&D and submission of project proposals to management. Second, the project is subdivided into professional areas. Third, conduct feasibility studies and explore different technical solutions. Fourth, develop solutions based on agreed work technology.
The external enterprise from 3GPP provides the concept proposal to 3GPP through the approval phase and then the technical reporting phase, and finally enters the product development phase. Sometimes, 3GPP will propose a modification request. That is to say, it has to go through five stages: from vision and concept to project proposal to feasibility study project, development work project and commercial deployment phase.
Unlike many people's imaginations, most of the technical decisions of 3GPP are not formed by voting at the conference. Its decisions are driven by technology and come from processes that are based on consensus and open to all members.
The 3GPP members propose different solutions and technologies through the “Proposalâ€, and then the proposal is openly discussed at the 3GPP meeting. Then, any member can object to a proposal at any time (that is, it can continue to be outside the 3GPP meeting) A proposal and an alternative proposal are discussed. Finally, most of the 3GPP technical reports and technical specifications are the results of changes made by 3GPP members based on the original proposal. The process is full of discussion and negotiation.
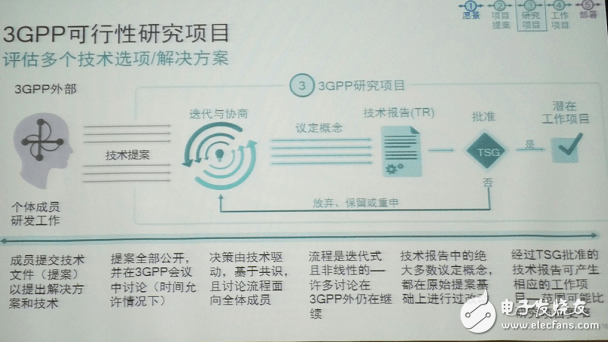
It is reported that 3GPP proposals have different types, such as concept proposals, modification requests, and so on. For 3GPP, the quality of the proposal is more than the number, because not all proposals have equal value. 3GPP technical decisions and norms are not established by accepting or opposing the direct mechanisms of individual proposals, but rather by progressive collaboration of specific core concepts. Furthermore, it is difficult to assess the impact of a single technical proposal, many of which focus on one feature or a part of a study and are therefore difficult to standardize.
In the view of 3GPP, technical proposals are not scientific by number. Because cellular technology is built on the work technology done in the past 3GPP and the entire industry. There may be another situation where member companies will award incentives to their 3GPP representatives to maximize the number of proposals. In addition, the database is built for engineers and is not suitable for macro analysis, which is prone to different interpretations.
Technical specifications are the final result of the completion of 3GPP workCurrently, 3GPP has more than 1,200 active 3GPP technical specifications; each specification is based on hundreds of submitted proposals; each proposal has at least one reporter (editor and manager), following the guidance of the working group The technical specification group is responsible for freezing the functionally stable specifications at the quarterly meeting, and downstream manufacturers reusing the technical specifications for product development.
The specification is identified by a 5-digit number that classifies the specification into meaningful technical categories.

3GPP introduces the latest technical features into cellular systems through Release, which is similar to different versions of mainstream operating systems. New features are introduced through different 3GPP Releases. For example, 4G LTE continues to evolve in more than 8 different versions.

The 3GPP specification evolves in a highly iterative manner, but builds on previous versions to support backward compatibility. For example, an LTE Rel-10 user equipment can operate at an LTE Rel-8 base station. Conversely, the LTE Rel-8 user equipment can also work in the LTE Rel-10 base station.
In summary, the new features of wireless communication technology can be introduced through different 3GPP Rel. Including, measuring the actual process: the new feature is functionally frozen and can be put into deployment. Also includes auto-sensing: build a system based on a set of freeze specifications in a version. And interleaved: work in different phases of multiple versions of 3GPP can be deployed in parallel. Iteration: The version includes more than the newly completed features, and each version is built on top of the previous version.
Enterprises and standardization organizations complement each otherCurrently, 3GPP is driving the development of 5G, and all members of the organization are actively engaged in the next generation of wireless communication technology. There is no shortage of communication giants in the standardization organization. Many influential industry giants, such as Qualcomm, Huawei, and ZTE, are actively promoting the development of 5G.
Standards have always been a must for communications companies. At present, the air interface standard in the 5G era has not yet been determined. 3GPP is stepping up the development of 5G new air interface standards. Next, around the 5G new air interface standard, each equipment supplier will have some competition.
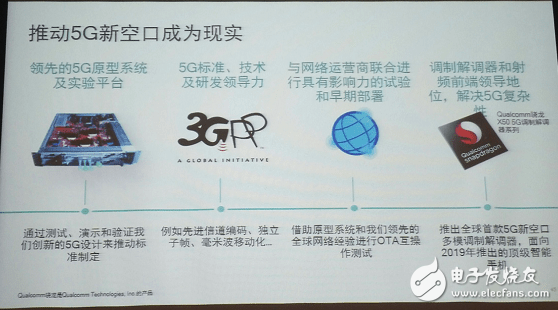
Qualcomm has taken the lead and has completed the first 5G connection based on 3GPP 5G new air interface (5G NR) standard. It is widely believed that Qualcomm's 5G new air interface is expected to become the global 5G standard. It is reported that the 5G connection is completed by Qualcomm's 5G new air interface prototype system below 6GHz, demonstrating that the 5G new air interface technology can efficiently achieve multi-gigabit data rate per second and significantly reduce latency compared to today's 4G LTE network. The 5G new air interface prototype system can operate based on the intermediate frequency band of 3.3GHz to 5.0GHz. The successful completion of the connection is an important milestone in the large-scale rapid verification and commercial process of 5G new air interface technology.
At the same time, Qualcomm has also developed a number of key 5G technologies. There are corresponding research and deployment on 5G key technologies such as Gigabit LTE, channel coding, independent subframe, millimeter wave mobility, and massive MIMO. Conduct influential trials and early deployments with network operators. In addition, the world's first 5G NR multimode modem X50 was released, which laid the foundation for 5G commercial use.
In terms of 5G standards, technology and R&D, Qualcomm has always maintained a leading position. It is reported that Qualcomm has invested R$46 billion in R&D for 5G. In the next work, Qualcomm plans to simultaneously perform 5G new air interface non-independent mode (NSA Mode) and 5G new air interface independent mode (SA Mode). It is planned to complete the deployment of NSA Mode in R15 at the end of 2017, which is considered by Qualcomm as a medium-term milestone. And it is planned to complete the SA Mode standard specification by the end of R15 in mid-2018.
Pvc Conduit Pipe,Plastic Conduit Pipe,Electrical Wiring Pipe,Plastic Cable Conduit
FOSHAN SHUNDE LANGLI HARDWARE ELECTRICAL CO.LTD , https://www.langliplastic.com