Multimedia product designers must provide high-quality audio effects, including high-output speaker modes. These places even need the system's audio amplifier.
The efficiency of the linear amplifier is 50%, so a slight increase in output power will result in a large increase in current consumption and excessive heat dissipation, resulting in the need for a large heat sink. In car audio systems, space and cost are very valuable, so the cost of these heat dissipation factors is quite expensive.
However, Class D amplifiers have the greatest power consumption when the output power is at its maximum. When playing music, the amplifier reaches the peak output power time is very short, thus reducing the RMS output power. This feature makes it possible to use a much smaller heat sink than linear amplifiers, and thus becomes a great advantage for automotive OEMs. The main unit can provide additional output channels without the need for expensive external amplifiers. In addition, there is a fairly high sound quality, the cost of packaging and heat generators is minimized, and there is a saving in power.
The heat sink for Class D amplifiers can be safely sized based on the half-peak output power. However, designers must still determine the exact size, cost, and application of the heat sink. The PCB design of the amplifier can also be used to reduce heat dissipation. Using copper pads for large-scale integrated circuits and all the widest PC traces connected to the IC can minimize power consumption.
Class D output transistors operate in a switching mode from all "on" to all "off" and take very little time in the linear region, so very little power is used for heat loss. If the resistance of the transistors is very low, the voltage drop through them is small, which will further reduce power consumption.
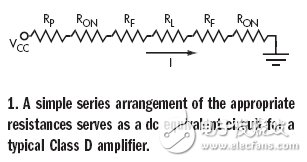
The DC equivalent circuit of a typical Class D amplifier with two transistors "on" is just a series of series resistors: RON, the output conduction loss of each transistor; RP, the addition of metal interconnections, lead structures, and PC board traces Resistance; PL, load resistance (Figure 1). Another cause of power loss is the switching delay in the output resistor (Figure 2). The efficiency of the entire system can be estimated as follows:
![]()
For example, suppose that a dual-channel Class D amplifier driving a 4Ω bass amplifier is operated in an environment of 60 ° C with an efficiency of 90% of full power, does not require a 14V DC Power Supply, and has a 5 ° / W IC junction resistance ΘJA). For a sinusoidal signal, the output peak current limit is:
![]()
This is consistent with PLOAD PEAK = "I2PEAKRL" = 49W / channel output peak power, and PLOAD RMS = "PLOAD" PEAK / 2 = 24.5W / channel RMS output power. Use the efficiency formula:
![]()
The total heat dissipation is about 6W.
The highest junction temperature is not directly related to the performance of the amplifier. However, the junction temperature is very important to determine the size of the heat sink, because a higher TJ can handle higher power consumption. The temperature of the mold is TJ = TA + PDISS & TImes; ΘJA = 90 ℃, this value is less than the maximum junction temperature of the device 150 ℃.
In the practical example of using a music signal, the designer must consider the maximum amplitude (crest factor) of the average value of the signal. The crest factor of a typical music signal is 3 ~ 10. Taking decibel as a unit, it is 10 ~ 20dB [PdB = 20log10 (VPEAK / VREF)]. So in order to allow the largest part of the music signal to pass without distortion, the amplifier requires 10 ~ 20dB of dynamic space relative to the general power output.
When the operating voltage of the class D amplifier is 14V, a peak value of 98W may appear. The conversion to decibels is:

Subtracting the crest factor limitation, the average sound level of the undistorted output can be obtained:

Convert to RMS output power:

When the PPEAK is 98W and the RMS output power is 955mW, the total power consumption is 0.2W and the maximum junction temperature is 61 ° C. When the RMS output power is 10W, the total power consumption is 2.2W, and the maximum junction temperature is 71 ° C. Therefore, the maximum power consumption of an audio CD signal without distortion occurs when the average sound is 4dB.
These examples show that sinusoidal signals cause more power consumption than true audio signals. Therefore, the sinusoidal signal can be used as a load for extreme thermal testing, causing the amplifier to shut down due to heat.
High efficient charging speed for Lenovo and IBM laptop, stable current outlet can offer power for the laptop at the same time charge the laptop battery. The best choice for your replacement adapter. We can meet your specific requirement of the products, like label design. The plug type is US/UK/AU/EU.The material of these products is PC+ABS. All condition of our products is 100% brand new.
Our products built with input/output overvoltage protection, input/output overcurrent protection, over temperature protection, over power protection and short circuit protection. You can send more details of this product, so that we can offer best service to you!
Lenovo Adapter,Charger For Lenovo,Power Supply For Lenovo,Adapter For Lenovo Mini
Shenzhen Waweis Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.waweis.com