Flip-chip LED filaments have become the focus of market research due to their flip-chip and planar coating processes and 360° stereo illumination.
For a long time, experts at home and abroad have devoted themselves to the study of the uniformity of illumination of LEDs. However, LEDs are a comprehensive system in which light, electricity and heat interact with each other. The optical performance of the output is affected by the input current and junction temperature.
When the minority carriers injected into the PN junction of the LED are combined with the majority carriers, the excess energy is released as light, and the electrical energy is directly converted into light energy, but in the process, a large amount of heat is generated. If the heat cannot be dissipated in time, the temperature of the PN junction will rise rapidly, which will affect the illuminating performance of the flip-chip LED filament.
In this paper, the law of the output light and color temperature of the inverted LED filament driven by different DC currents with the input current and temperature is studied. The luminous flux and color temperature of the initial state and steady state (after lighting for 30 minutes) are compared. The effect of optical performance.
1. Sample preparation and testing
1.1 Sample preparation
The flip-chip LED chip is fixed on a white ceramic substrate by a die bonder. The size of the ceramic substrate is 60 mm × 1.2 mm × 0.38 mm, and the chip size is 12 mil × 26 mil. The filament is dispensed by a two-layer coating method. . Six filaments prepared by the above method were taken, and six filaments were connected in series, and the sample was as shown in FIG.

1.2 Testing
The luminous flux, color temperature and color coordinates were measured using an integrating sphere of the model ZWL-9200. The LED to be tested is placed in the center of the integrating sphere by a fixed fixture. The light emitted by the LED passes through the white diffuse reflection layer inside the integrating sphere, and a part of the light is diffused and transmitted through the aperture aperture fiber on the surface of the integrating sphere to the micro multi-channel spectrometer. The data collected by the spectrometer passes. The USB interface is sent to the computer for processing and display, and the light source is powered by a constant current source.
2. Analysis and discussion
The test was carried out using a Chinese integrating sphere. The sample is illuminated, placed in the integrating sphere, and tested for transient color temperature, luminous flux, and chromaticity coordinates. After lighting for 30 min, measurements were taken again to obtain steady-state optical performance. Subsequently, the transient and steady state data were analyzed and compared to arrive at a conclusion.
2.1 Luminous flux analysis
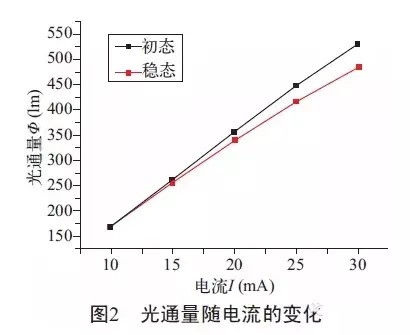
The change of luminous flux with current is shown in Fig. 2. Whether it is in the initial state or steady state, the luminous flux increases with the increase of current. This is because the PN junction is the core part of the light-emitting diode. After the current is increased, the number of electrons and holes injected into the light-emitting region increases, and the amount of radiation recombination increases, resulting in an increase in the luminous flux of the LED. In theory, the luminous flux of an LED increases linearly with increasing current.
However, as shown in Fig. 2, in the initial state and the current is 10~25 mA, the change of the luminous flux with the current is a straight line with a slope of K=18, and the current and the luminous flux are almost linear, and at 25~30. At mA, the slope K = 16.1313, with a significant drop.
24V Pwm Solar Charge Controller,Solar Mppt Controller,Power Inverter With Charger
GuangZhou HanFong New Energy Technology Co. , Ltd. , https://www.hfsolarenergy.com