Mobile TV refers to broadcasting using digital broadcasting technology. The receiving terminal is an on-board mobile TV installed on buses, subways, trains, taxis, private cars and other vehicles, and the second is a mobile phone, PMP, notebook computer, ultra-portable PC And other portable devices to meet the needs of the mobile crowd to watch TV programs. <>
The terrestrial digital TV standards for mobile TV applications mainly include DVB-T, ATSC and ISDB-T. DVB-T standards are mainly concentrated in Europe, ISDB-T is only adopted by Japan, and ATSC is mainly distributed in North America. China's terrestrial transmission standard is basically determined, but its actual implementation will take time. At present, DMB-T of Tsinghua University, ADTB-T of Shanghai Jiaotong University, STIMi of Institute of Broadcasting Science (Guangdong Academy of Sciences), and DVB-T of Europe have entered industrialization in the digital terrestrial transmission standard of China. There are about 43 provinces and cities in China that have launched or experimented with terrestrial transmission mobile TV. Among these areas, Tsinghua ’s DMB-T and European DVB-T standards are the most used, and Shanghai Jiaotong University ’s ADTB-T standard is still mainly Shanghai.
There are two types of networks for transmitting mobile TV programs, one is based on mobile communication networks, and the other is based on broadcast networks. These two types of mobile TV have their own advantages and disadvantages. The mobile communication network is more convenient to provide personalized services, but its bandwidth is limited and the cost is higher. The development of the broadcast and television network must precede the mobile communication network, but its biggest problem may be the constant disputes of multiple standards. Currently, the world's major handheld device TV broadcast standards include DVB-H in Europe, T-DMB in South Korea, ISDB-T in Japan, and Media FLO from Qualcomm in the United States.
China's mobile TV standards have diversified trends, including the industry standard CMMB (STIMi is the core) launched by the State Administration of Radio, Film and Television, T-MMB of Beijing New Shoreline Company, DMB-T / H of Tsinghua University, CMB proposed by Huawei, The CDMB proposed by the Communications and Broadcasting Standardization Committee, as well as the European standard DVB-H, the Korean standard T-DMB, and Qualcomm's MediaFLO. Since it is not yet clear which (or several) standards will become China's mobile TV standards, handheld TV solution providers still seek entry points with multimode and multiband.
Table 1 lists the main mobile TV standards and their main features. From the perspective of the front-end solutions currently provided, the largest number of semiconductor companies support the DVB-H standard, including Freescale, TI, Microtune, Samsung, Broadcom, DiBcom, Frontier Silicon, Siano Mobile, Newport Media, NXP, etc. The main manufacturers supporting T-DMB standard are Frontier Silicon, Sinao, Newport Media, Zhuo Sheng Microelectronics, etc. The manufacturers supporting ISBD-T are mainly Japanese manufacturers and companies such as TI, Newport Media and Qualcomm. Qualcomm, Newport Media and others support MediaFLO.
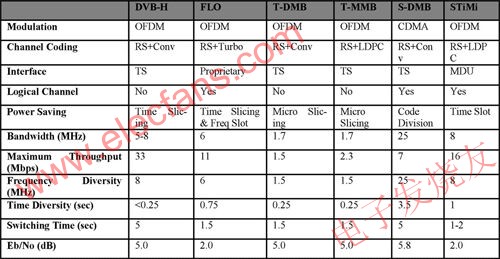
Table 1: Main mobile TV standards and their main features.
This article will focus on the design challenges of mobile TV systems, as well as design methods and techniques, and comprehensively introduce the mobile TV solutions of major semiconductor manufacturers, including tuners, demodulators, media processors, and single-chip and multi-chip solutions.
Mobile TV: Mobile TV system, power consumption, receiving sensitivity, mobile speed limit are three major difficulties
From the earliest pure voice communication function to the ability to play MP3 music, video recording and playback, megapixel photography, and now the most popular support for dual mode / multimode, GPS positioning navigation, Wi-Fi-based VoIP, RFID automatic payment, now The small mobile phones that people carry with them contain almost all the main functions of small electronic devices. This makes the system design of mobile phones more and more complicated. Design engineers must not only place more antennas, RF switches, power amplifiers (PA), and filters in thin and light mobile phones, but also deal with more severe power consumption problems, and face how to solve the switching and radio frequency of multi-mode mobile phones. Isolation, how to improve the receiving sensitivity, how to achieve extended battery life and so on. The addition of mobile TV functions undoubtedly makes these all more severe.
"There are four key challenges in the design of mobile digital TV: small form factor, power efficiency, high linearity, and achieving advanced performance," said James Kamke, vice president of marketing and sales at Newport Media. Fairchild Semiconductor's signal path product line product marketing manager Han Xiaoyong also pointed out that power consumption, receiving sensitivity, and moving speed limitations are three major difficulties.
First, because mobile TV customers require at least 3-4 hours of continuous operating time, designers must consider the battery life of the product. Secondly, whether the mobile TV can successfully receive the broadcast signal is critical, otherwise it will cause other competing solutions (such as satellite solutions) to join the competition and win some supporters. Finally, since mobile TV equipment and customers move at a higher speed together, the signal timing will be forced to change due to the Doppler effect, which will cause difficulties in reception and decoding.
To solve these challenges, a small-sized modular design should be adopted for the MTV subsystem, but this module can have different architectures in different end products. For mobile phones, the best architecture for implementing MTV functions may be the use of mobile phone chips + MTV SoC. MTV SoC usually integrates multiple demultiplexers and ARM processors to offload the mobile phone chip. For PMP, the best architecture is to use a simpler MTV chip (such as integrated RF and demodulator only) + media processor, or RF + demodulator + media processor. This can reduce system-level costs. For laptops, the best way is to use a USB dongle with MTV function.
Han Xiaoyong pointed out that the best architecture for mobile TV is to connect the TV module (including tuner, demodulator and A / V decoder) of the portable main CPU via the SDIO interface, because this solution has the least changes to the existing system . Similarly, functional modules can be added or removed from the complete system to reduce the design difficulty as much as possible.
Wang Wei, general manager of Siano Mobile Silicon China, believes that the chip architecture must be feasible and efficient at the system level. High efficiency means that the chip can achieve low power consumption and small size, and feasibility means that the chip can provide a common hardware interface and flexible and diverse software interface, so as to be compatible with different mobile digital TV (MDTV) standards, different background processors and The operating system matches.
The following analyzes the technical challenges, implementation difficulties and mainstream semiconductor solutions faced by each functional block of the system.
As shown in Figure 2, a mobile phone system with mobile TV broadcasting function is mainly composed of three subsystems: a communication subsystem, an application subsystem, and a mobile receiving subsystem. The mobile TV receiving system is mainly composed of an antenna, a tuner, and a decoder. In addition, the parts related to the mobile TV function include an application processor, a controller, and a display screen.
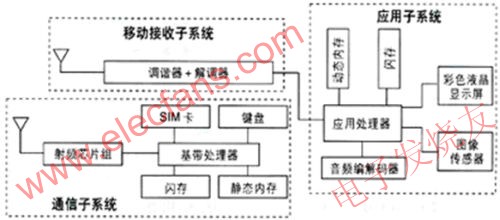
Figure 2: The TV mobile phone system is mainly composed of a communication subsystem, an application subsystem and a mobile receiving subsystem.
1. Antenna
The signal chain starts with an antenna, which is very important for mobile TVs that rely on terrestrial broadcast signals. If the device receives both VHF (channels 2-13) and UHF (channels 14-83), then the antenna must handle wavelengths from 5.5 meters to 34 centimeters. Therefore, even in terms of half or quarter wavelength, the device size cannot be large enough to support a fully integrated antenna, especially in the VHF band.
"The antenna design is very challenging, especially the DVB-T antenna in notebook computers. The built-in antenna is one of the popular mobile TV functions of portable electronic devices, but designing an antenna that can meet the gain requirements of the VHF and UHF bands But it's very difficult. "Broadcom's mobile TV product marketing manager Chris Cytera said.
"Today's technology trend is toward the direction of fully integrated antennas, which puts higher demands on the design. One way to increase the gain of the system is to use tunable antennas, which ensure the best gain in each frequency band. "Mark Hopgood, director of business development at Frontier Silicon, said.
When arranging the antenna of a mobile TV, it is critical to consider the body effect of the user who watches the TV while holding the phone. Using intelligent tunable antenna design helps optimize signal reception as the environment changes continuously. In order to maximize the gain and at the same time minimize the interference of mobile phone noise, it is also important to maintain a reasonable spatial distance around the integrated antenna.
2. Separate tuner and demodulator solution
Tuner and decoder are important parts of the mobile TV receiving subsystem. The antenna transmits the RF signal to the tuner, which can amplify the input and convert it into a video signal suitable for the decoder level. The importance of the tuner is that it has a great influence on the overall size of the device and battery consumption. The next part of the signal chain after the tuner is the decoder, which digitizes the TV signal and may do some processing.
There are two schemes for tuning and demodulation: one is that the two are separate chips, and the other is single-chip integration. In the early days, in order to quickly launch a solution, some manufacturers chose a separation solution.
Freescale provides a separation solution that uses the company's MC44CD0I / 02 for the UHF band (430-862MHz) and the MC44CD03 for the US L-band (1.67GHz), coupled with DiBcom's DIB7000-H chip. DIB7000-H is the world's first mass-produced demodulator that supports DVB-H mobile reception specifications.
Microtune also launched a separation solution. Its dual-band DVB-H tuner chip MT2260 uses an integrated design without the need for an external low-noise amplifier (LNA) or balun. The typical power consumption in viewing mode is 20-40mW. The frequency bands that MT2260 can currently receive are the L-band in the United States and the UHF band in Europe (470-8? 0MHz).
Samsung ’s DVB-H front-end chipset has a Zero-IF (intermediate frequency) CMOS RF tuner (S5M8600), as well as a channel decoder (S3C4F10), CPU and built-in memory that comply with DVB-H / T standards The system is also more characteristic, using a dual-chip solution of SC32442 application processor plus SA3A480 H.26? Decoder.
Broadcom's BCM2900 is a monolithic zero-IF tuner using 0.18μm CMOS process, and supports DVB-H, DMB-T and DMB-TH standards. Because it supports the UHF, IV, V, and L bands used in the European standard 1450 MHz to 1490 MHz frequency range and the U.S. 1670 MHz to 1675 MHz frequency range, the device is suitable for digital TV reception in portable devices almost anywhere in the world.
ADI and Legend Silicon (Legend Silicon) jointly launched the industry's first mobile TV receiver solution that complies with the Chinese digital TV terrestrial broadcasting standard DMB-TH. The platform integrates ADI's Integrrant low-power RF tuner and Lingxun's demodulator. Using Integrant's tuner, ADI provides the platform with the industry's lowest power RF tuner to maximize battery efficiency while its small package can meet the requirements of small size and low cost. The company's DMB-TH standard demodulator (Demodulator) adopts a new design. The tuner for mobile TV is the second generation chip (LS8? 13) designed for receiving DMB-TH. In addition, ADI has adopted its low-power Blackfin processor to complete MPEG-2 decoding and multimedia processing functions in mobile TV applications.
"Integrating a CMOS direct conversion tuner and demodulator on the same chip achieves the best architecture for these devices. A hard-wired demodulator architecture minimizes power consumption / die area because it does not require" soft " The cost of instruction decoding in the solution. "Broadcom's mobile TV product marketing manager Chris Cytera said. Due to the CMOS process and direct conversion architecture, the BCM2900 does not require external IF, image suppression filters, and any tunable components. The BCM2900 is suitable for low-cost mobile TV solutions, such as PC TV tuner cards.
Some separate tuner and demodulator solutions also include: Qualcomm ’s Universal Broadcast Modem (UBM) that supports FLO technology, DVB-H and ISDB-T; Zhuosheng Microelectronics specifically designed for DAB, DAB-IP and Mobile digital TV demodulation chip MXD0120 designed for T-DMB application; IF101, the world's first mobile TV channel demodulation chip that complies with the CMMB standard, launched by Chuangyi Videoconferencing.
3. Integrated tuner and demodulator solution
As system manufacturers need complete receiver solutions, more and more tuners and demodulators are packaged together. In addition, most suppliers are quickly turning to next-generation tuner or demodulator ICs that can handle multiple mobile TV standards to meet changing market demands.
"How to make the best compromise between small size, low power consumption and high performance (ie high sensitivity, linearity, noise and interference resistance) is a design challenge for TV phones." Azzedine Boubguira, Vice President of Marketing and Business Development, DiBcom, " To solve these problems, the first stage is to realize the integration of the RF tuner, demodulator and most discrete devices in the same small package. "
DiBcom targets products in different mobile TV markets such as automobiles, mobile phones, PCs and laptops, PMPs, navigation devices, set-top boxes, LCD TVs, etc. Most of them have integrated multi-band RF tuner and demodulator, support DVB-H, DVB-T, DVB-SH, T-DMB and ISDB-T standards.
Frontier Silicon's Apollo FS1110 is a tri-band dual-mode RF front-end receiver suitable for broadcasting digital radios and mobile TVs, such as T-DMB and DAB. The combination of Apollo and Frontier Silicon's Kino digital baseband chip can realize a complete set of optimized RF and baseband T-DMB solutions on mobile phones and other devices. Apollo can also use the company's DVB-T / T-DMB / DAB multi-standard baseband receiver chip Paradiso. Paradiso is developed from Frontier Silicon's Kinot and Chorus products (for T-DMB and DAB) and supports all DVB-H and T-DMB formats, including variants in China, Europe and South Korea. Figure 3 shows the block diagram of the mobile TV system based on Paradiso 1T.
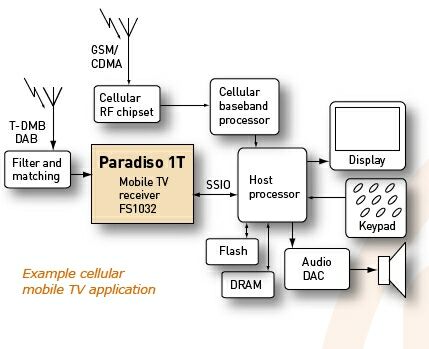
Figure 3: Block diagram of a mobile TV system based on Paradiso 1T.
The advantage of the Frontier Silicon solution is that it uses an intelligent interference suppression mechanism. Under adverse objective conditions, such as GSM / CDMA noise affecting other frequencies, it can ensure the best signal reception sensitivity; when there is noise interference on the channel, Adopt the co-channel interference cancellation mechanism to ensure high receiving sensitivity; it has a high signal attenuation / crosstalk ratio (ACR), which can ensure that the receiver continues to maintain a good working state, even near the MDTV transmitter; it is very high for DVB-H Doppler performance (over MBRAI 2.0).
TI also adopted an integrated solution. Its Hollywood single-chip solution is the industry's first chip that uses a standard 90nm digital process to integrate a mobile TV tuner with a demodulator. Among them, DTV1000 and DTV1001 are the first products of Hollywood single-chip series, supporting open industry standards, including DVB-H used in Europe, the United States and parts of Asia, and ISDB-T used in Japan. Interface to TI OMAP series application processors.
The Israeli company Siano Mobile's SMS1000 is also an integrated solution, including the SMS1001 tuner and SMS1002 demodulator chip. SMS1000 supports multiple standards (DVB-H, DVB-T, T-DMB, DAB, EPM-DAB) and multiple bands (VHFIII, UHF, L1, L2), and provides SPI, SDIO, USB 2.0, GSP interfaces. The company's single-chip receiver SMS1010 supports standards such as DVB-T, DVB-H, T-DMB, DAB, and DAB-IP, as well as four different frequency bands. It integrates an RF tuner and demodulator, and the average power consumption in DVB-H mode is less than 22mW. The biggest difference with other competing solutions is that SMS1010 does not require external memory or VCO. Figure 4 is a block diagram of a mobile phone TV system using SMS1010.
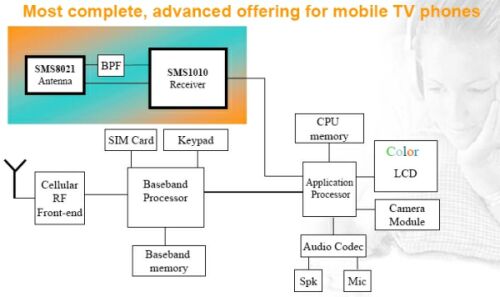
Figure 4: Block diagram of a mobile TV system using SMS1010.
Newport Media's single-chip mobile TV receiver NMI310 has a high degree of integration, it integrates an RF tuner, demodulator and all necessary storage modules. The chip can demodulate signals using DVB-H, DVB-T, T-DMB, ISDB-T, MediaFlo and other standards. NMI310 integrates a four-band, direct conversion receiver and a DVB-H demodulator and all necessary memory. The chip can simultaneously receive 8 signals, and the power consumption is only 20 milliwatts. In addition, it has a variety of characteristics, such as the suppression of adjacent channel signals up to 55-dB, which can purify the picture so that users can get the best visual effect.
PN3030 of PnpNetwork of South Korea is a DMB receiver that meets ETSI EN 300 401 and T-DMB standards. The device has low power consumption and a small package size (8x8x1.5mm 80LFBGA), and is suitable for handheld devices for a variety of mobile digital TV solutions, such as mobile phones and portable audio and video equipment. It supports I2C, I2S, SPDIF, SPI, HPI, MPEG-2 TS and RDI standards to meet the needs of different applications.
NXP Semiconductors (NXP) has adopted a compromise SiP solution. BGT210 and BGT211 are low-power DVB-H front-end chips. BGT210 serves the European market and BGT211 serves the US market. The chip contains a TV tuner (TDA18281 / 2), programmable channel decoder / demodulator (TDA10105), source decoder, and complete software package for DVB-H transmission control, file transmission, and real-time A / V transmission .
4. Application processor and media processor
Mobile TV may be implemented in two ways: broadcast and video streaming, but not all mobile media processors can support both mobile TV at the same time, because the current mainstream mobile TV standards such as DVB-H and T-DMB use What is H.26? Or VC-1 (required by the United States) codec mode, and the video stream based on mobile network mainly uses the MPEG4 codec mode. In addition, electronic program guide (EPG), transport stream demultiplexing, real-time streaming video / audio / MEPG decoding, TV functions (such as closed captioning (CC), teletext, etc.) are additional functions for mobile phones It was not considered in the initial design of the mobile phone application processor, so the mobile phone application processor and the media processor should have more powerful processing functions.
"Meeting the media processing functions of mobile TV requires four prerequisites: 1) low power consumption and low cost; 2) supports D1 and enables real-time encoding and decoding on a small screen; 3) highly integrated SoC; 4) support Multiple media standards. "Cary Ussery, President and CEO of Vivace Semiconductor, said," The current market solutions do not fully meet the needs of mobile TV equipment. Single-chip processors or CPU + DSP It is difficult for the structure to meet multiple needs of low power consumption, D1 support and high integration at the same time. "
The media processing function provided by Xinhui can support various standards such as DVB-H, T-DMB, DMB-TH, T-MMB and STiMi. It has high performance and is the most optimized product to meet the needs of the portable video playback market. . The company currently offers two highly integrated products. One is the VSP100 chip, which is an ideal low-cost product designed for the next generation of portable media devices. The other is the VSP200 chip, which provides higher performance and is the most optimized product to meet the needs of the portable video playback market.
The advantage of Beijing C2 Microsystems' CC1100 media processor is that it can provide an ideal PMP platform solution. It supports MPEG-2, H.26? (BP & MP), MPEG-4.2 (ASP), VC-1, RM, Flash, MJEPG and other video format encoding and decoding and transcoding. The MPEG-2 decoding image quality can reach high definition (720p / 1080i), and the encoding and decoding and transcoding quality of other formats can reach standard definition (D1). PMP based on the CC1100 media processor can easily integrate MTV functions.
Broadcom ’s VideoCore mobile multimedia processor supports Microsoft ’s Windows Media Video (Microsoft ’s video compression standard, often referred to as VC-1), which will effectively promote the launch of new mobile TV services by US operators in 2006. This support also means that Broadcom's VideoCore series of mobile multimedia processors intends to advance into the next generation of mobile phones and portable multimedia players that are ready to receive DVB-H and other formats of mobile TV content. The BCM2702, BCM2722 and BCM2724 chips based on Broadcom ’s VideoCore technology support all mobile multimedia application standards, including VC-1 and H.26 ™ (MPEG-4 AVC) video codecs, as well as all audio codec standards, such as AAC + , WMA and BSAC. This flexibility and programmability make this series of processors very suitable for any mobile TV standard being deployed, and it is possible to develop a truly global multi-standard mobile TV receiver. In addition to supporting many technologies, the VideoCore processor also provides industry-leading power consumption performance, it has the ability to decode VC-1 and H.26? Video, and consumes less than 150mW of power. Compared with traditional software-based solutions, the performance of this programmable solution allows longer mobile TV viewing time and battery life.
nVidia is currently the world's major mobile TV mobile phone-Samsung DVB-H mobile phone processor supplier, nVidia processor has been used in the design of many TD mobile phones, including international manufacturers and local manufacturers. But nVidia processors GoForce 4000 and GoForce 5500 do not support the AVS standard. If China's CMMB standard adopts AVS, nVidia will also need to redesign the chip.
ST's Nomadik multimedia application processor product line utilizes a unique architecture with distributed sound and image accelerators as the core. In addition to the functions of mobile phones for watching mobile TV, smart phones, multimedia phones, PDAs, network appliances and car entertainment systems The audio and video and image processing functions of related terminal products can be provided through the Nomadik multimedia processor. Figure 5 is a functional diagram of the Nomadik multimedia application processor.
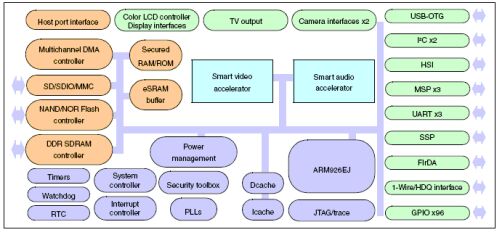
Figure 5: Functional diagram of Nomadik multimedia application processor.
When supporting multiple codec formats, processors based on ARM or DSP soft decoding are very advantageous. Such as TI's OMAP and Freescale's i.MX31, etc., they can be easily upgraded without redevelopment. However, if you want to consider performance, power consumption and cost, processors based on hard logic are more popular, such as nVidia's GoForce 4000 and GoForce5500 and SMedia's Glamo 3370 and Glamo 3360. But the former is also adopting a compromise method, that is, H.26? And MPEG4 adopt hard accelerators, such as TI's OMAP, Freescale's i.MX31, Jade's X900, Fuhan Microelectronics' FH8800 and nVidia's GoForce 6100, etc. . Design engineers need to weigh many factors when choosing a processor for mobile TV.
Car mobile TV: improving reception quality is the key
Car mobile TV is mainly composed of set-top box (such as DMB-T set-top box), LCD screen, antenna, car power supply and so on. The set-top box converts the radio frequency signal received by the antenna into an intermediate frequency or baseband modulation signal that the demodulator can receive; after the demodulator receives these signals, it decodes it and outputs it as a code stream containing broadcast data; and then demultiplexes the broadcast data from Separate from other code stream signals, and select the audio and video data corresponding to this machine to download or play in real time from the separated signals according to the control information; then process other multimedia information and finally display it on the car TV come out.
Car TVs do not have high requirements for power consumption, but because DVB-T is designed for mobile reception, a multi-antenna "diversity" system is required to obtain satisfactory in-car TV reception. For example, using "scan diversity" technology, the system controls the switching between different antennas and selects the antenna with the highest reception level to obtain satisfactory image quality.
It is recommended that DVB-T receiver antennas use maximum ratio combining (MRC) diversity to combine the best carrier signals to form an output signal. Even if the vehicle's operating speed exceeds 100Km / h, it can ensure good reception quality for car TVs. The function of frequency diversity is independent of antenna diversity. During the reception process, the hybrid TV receiver scans the transmitter without any operation on the user part. If a channel is found to carry the same content, but the reception quality is better, the device will automatically switch to this new channel. In this way, users can watch programs continuously while traveling, without having to manually tune when the car passes a certain launch station coverage.
Laptop PC TV solution
Watching TV programs through a computer is not a new thing. As early as more than 10 years ago, you can buy a TV card with a PCI interface from the market and plug it into a desktop computer to watch analog TV programs. But at that time, the effect of watching TV on the computer was not satisfactory, and installing a TV card was also quite laborious. Nowadays, as the processing speed of PC products is getting faster and faster, and the built-in wireless, Bluetooth, and graphics card functions are becoming more and more powerful, and have more and more multimedia audio and video playback functions, people want to personally The entertainment experience of watching TV programs can also be obtained on the computer. InStat predicts that by 2009, the retail sales of PC TV tuner cards in the global market will reach 3.7 billion US dollars, with an average annual compound growth rate of 42.6%.
The interface of the PC TV tuner card is also PCI (for desktop computers), PCI Express (for desktop computers and notebook computers), USB (for laptop computers), so system solution providers must design PC TV for different markets Tuning card.
Zeng Qingfeng, marketing manager of NXP Semiconductors ’Display System Solutions (China), said,“ Last year, PCI interface TV cards accounted for 70% of the Chinese market. This year, the PC TV market will continue to use mainstream PCI interfaces, but more are expected Of USB cards and PCI Express are emerging to meet the needs of mobile applications. "
NXP is currently the only supplier with all the key components of PC TV tuner cards, including AV decoders, channel decoders, tuners, and drivers. For example: OEM media center solution reference design for the North American market PCV500 uses NXP ’s SAA716? Or SAA716? Single-channel version SAA7163, and silicon tuner TDA18271, supports ATSC + NTSC or dual NTSC mode (dynamic dual mode); The PC TV solution for the European market uses the AV decoder SAA7131, silicon tuner TDA8275A and DVB-T channel decoder TDA10046; the PC TV solution for the Japanese market uses SAA7163, TDA18271 and channel decoder.
"For laptops, achieving good indoor reception quality is difficult, and using diversity technology (dual antennas) is very effective for improving indoor reception quality." Azzedine Boubguira, Vice President of Marketing and Business Development at DiBcom, believes.
DiBcom's "3-in-1" chip DIB7770 combines three functions into one, integrating three modules for receiving digital terrestrial television (DTT) on a PC: an embedded RF tuner, a demodulator, and a USB2.0 bridge. The development of this "3 in 1" program is to realize ultra-small and low-cost USB2.0 TV accessories that can receive high-quality digital TV. DIB7770 makes it possible to use either UHF or VHT (dual-band tuner), or a single mode or diversity mode (dual antenna) to receive a USB 2.0 solution. The dual-antenna scheme (diversity mode) can increase TV coverage by 50% in areas with limited reception, such as urban areas and indoors.
Micronas' USB2.0 interface PC TV MicStickD reference design allows consumers to watch and receive DVB-T video broadcasts and program schedule information on any desktop or laptop computer with a USB2.0 interface. The solution integrates a series of products, including DRX 3975D COFDM (Code Orthogonal Frequency Division Modulation) digital demodulator, Microtune MT2060 digital TV tuner and Cypress EZ-USB FX2LP controller. Micronas DRX 3975D is the first COFDM demodulator that conforms to NorDig-Unified V1.0.2 receiver specifications. MicStickD is fully compatible with existing DVB-T receiving system standards worldwide.
Trident's TV-Master is a highly integrated, high-speed USB2.0 convenient and convenient TV receiver chip. TV-Master provides a low-cost solution for watching TV based on a PC or laptop. The single IC of TV-Master integrates two channels of 16b audio ADC, two channels of 10b, 2D comb filter high-performance video decoders (video decoders) and an embedded MCU.
LME2510 is a USB2.0 digital TV control chip with optimized design. The main features include: USB2.0 interface; supports multiple digital TV standards, supports standard definition and high definition (HDTV) digital TV reception; built-in enhancements Model 8051 is compatible with MCU, supports user program download, and realizes differentiated functions; dual I2C interface, which can be individually controlled by RF Tuner and demodulation and decoding chips; built-in digital TV code stream processor, etc. Typical applications of the chip include computer TV (including notebook computers and desktop computers), handheld multimedia terminal digital TV, and digital TV reception of other computer equipment.
Zarlink ’s terrestrial digital TV demodulator ZL10355 can be used in PC-TV, portable and handheld digital TV receiver design. The device has the industry ’s smallest package, lowest power consumption and lowest software overhead, plus a wide temperature range Range, especially suitable for mobile DTV applications. The demodulator fully complies with the harsh NorDig Unified 1.0.2 standard. For more information, please log in to the electronic enthusiast website (http: //)
Moulded Case Circuit Breaker is MCCB , How to select good Molded Case Circuit Breaker suppliers? Korlen electric is your first choice. All moulded Case Circuit Breakers pass the CE.CB.SEMKO.SIRIM etc. Certificates.
Moulded Case Circuit Breaker /MCCB can be used to distribute electric power and protect power equipment against overload and short-current, and can change the circuit and start motor infrequently. The application of Moulded Case Circuit Breaker /MCCB is industrial.
Korlen electric also provide Miniature Circuit Breaker /MCB. Residual Current Circuit Breaker /RCCB. RCBO. LED Light and so on .
Molded Case Circuit Breaker
Molded Case Circuit Breaker,Small Size Molded Case Circuit Breaker,Electrical Molded Case Circuit Breaker,Automatic Molded Case Circuit Breaker
Wenzhou Korlen Electric Appliances Co., Ltd. , https://www.korlenelectric.com