According to IHS iSuppli's smartphone and converged equipment market research report, with the strong support of mobile network operators, the next generation 4G wireless standard-Long Term Evolution (LTE) will achieve amazing growth and growth rates this year and in the next few years It will be as high as several times or even dozens of times, and its number of users will reach a considerable level by 2015.
By the end of 2011, global 4G LTE users are expected to reach 11.6 million, a 4062% increase from the 300,000 in 2010. It is expected that this amazing growth will be maintained in 2012, with the number of users surged by 441% to 62.8 million.
In the three years after 2012, its growth will be slowed down, but it is still considerable: 215% in 2013, 105% in 2014, and 84% in 2015, as shown in Figure 2.
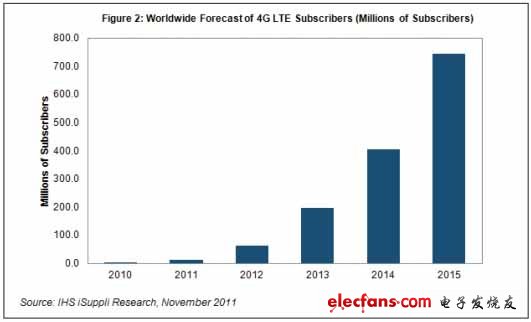
By 2015, just five years after its launch, the total number of LTE users will reach 744.2 million, accounting for 10% of the world's approximately 7.3 billion mobile phone users.
IHS iSuppli's data shows that although the number of LTE users will still be lower than those of older wireless technologies by 2015, such as 3.8 billion 2G users and 2.8 billion 3G users, the expansion rate of LTE will be unparalleled, especially It is the growth of the number of users of the old wireless standards that has continued to slow down.
People have different interpretations of 4G, but it is obvious that no matter which definition is adopted, the next generation of high-speed, low-latency wireless technology has come to us. The claimed speed is as high as 100Mb per second, and the delay is only tens of milliseconds. The average speed of this next-generation technology can theoretically reach 10 times the currently widely used 3G technology. 4G technology is particularly suitable for real-time applications with large data volume such as video transmission and multiplayer games. For older wireless technologies, these applications will quickly swallow bandwidth and capacity, making it difficult to transfer images and sound smoothly.
LTE has a long way to go
There is currently a universal air interface standard that the wireless ecosystem can use to develop next-generation smartphones, networks, and applications. This makes the rapid growth of LTE possible. In the past, there were multiple commercial standards for 2G and 3G technologies, which led to a fragmented market and constantly changing air interfaces, which not only confused users but also hindered the development of the entire industry.
However, as the wireless market matures, technology itself is no longer the difference factor that consumers value. Therefore, operators, mobile phone manufacturers and chipset suppliers no longer simply emphasize the technical parameters. Instead, they changed their focus and began to think in terms of usage / behavior. The high speed and low latency of the new technology can allow the device to do something. Attention is now focused on those product elements that can enhance the overall user experience, such as attractive mobile user interfaces, applications that can increase fun and productivity, and smooth integration with new cloud services.
It is true that the wireless industry still needs to face the previous decentralization of the air interface to ensure backward compatibility of future mobile phone devices. However, the consensus embodied in LTE means that the wireless industry can spend more time developing new applications and services for consumers.
The effect of using a common basic interface is emerging, and wireless technology is now a driving factor in many areas of business activity, including retail, services, banking, healthcare, and the automotive industry.
But IHS believes that operators still have to solve many technical and commercial issues. This includes a challenge related to the availability of continuous frequency bands. Operators can only use the 10MHz LTE channel instead of the more ideal and efficient 20MHz, and worse, the available frequency bands in different regions are completely different.
Other problems faced by operators include establishing new business models to accommodate the expansion of wireless technology into other industries; designing LTE devices that can take advantage of new chipset architectures; and coping with the rapidly changing environment caused by all these advances.
Precise Board to Board Connectors
Precise Board to Board Connectors,Floating Board to Board Connector,Board to Board Female Socket Connector,Female Board to Board Connector
Shenzhen Hongyian Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.hongyiancon.com