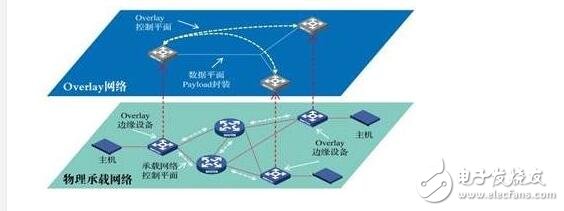
In the field of network technology, Overlay refers to a virtualization technology model superimposed on the network architecture. The general framework is to implement the application on the network under the condition that the basic network is not modified on a large scale, and can communicate with other networks. The business is separated and based on IP-based basic network technology. Overlay technology is to build a virtual network on top of the existing physical network, and the upper application is only related to the virtual network.
Overlay network composition:Edge device: refers to the device directly connected to the virtual machine.
Control plane: mainly responsible for the establishment and maintenance of virtual tunnels and the notification of host reachability information.
Forwarding plane: The physical network that carries the Overlay packet.
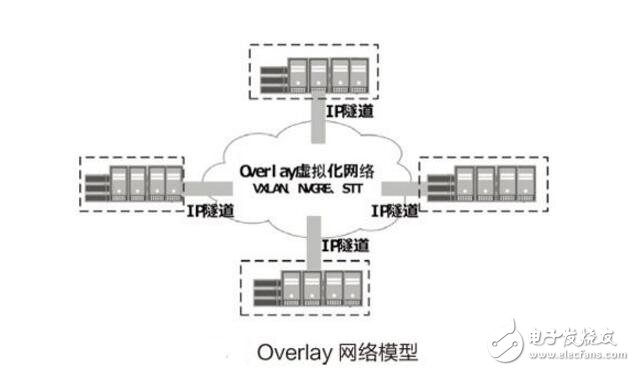
Overlay technology can be divided into three categories: network Overlay, Host Overlay and Hybrid Overlay. Network Overlay refers to network construction and extension of edge network devices through control protocols, which is the Overlay network technology described in this paper. Overlay network technology is diverse, and generally uses tunnel technologies such as TRILL, VxLan, GRE, and NVGRE. TRILL (Transparent InterconnecTIon of Lots of Links) technology is a new type of ring network technology promoted by telecom equipment manufacturers; NVGRE (Network VirtualizaTIon using Generic RouTIng EncapsulaTIon) STT (Stateless Transport Tunneling Protocol) is the Overlay technology promoted by IT vendors; and everyone is very familiar with Tunnel-based packaging technology such as VXLAN (Virtual eXtensible LAN). Since these are also new protocols, you need to upgrade your existing network devices to support them. The location of the application deployment in the Overlay network is not limited. The network device can be plug-and-play, automatically configured and delivered, and automatically run. The Overlay network service changes, the basic network is not perceived, and the traditional network is rarely modified. The most important thing is Both the virtual machine and the physical server can access the Overlay network.
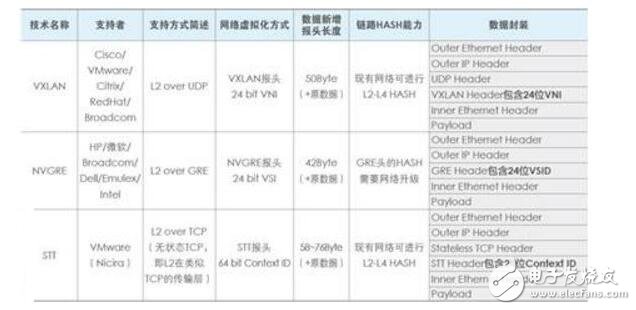
The current mainstream Overlay technologies mainly include VXLAN, GRE/NVGRE and STT. The three Layer 2 Overlay technologies generally carry Ethernet packets to a certain tunnel level. The difference lies in the selection and construction of tunnels, and the bottom layer is IP forwarding. A comparison of the key features of these three technologies is shown in the table below. Among them, VXLAN utilizes the existing universal UDP transmission, and its maturity is high. Overall comparison, VLXAN technology has relative advantages.
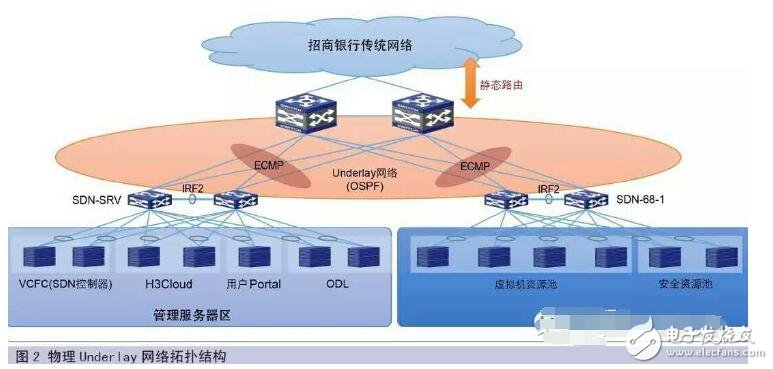
Ethernet is designed from the very beginning as a distributed network. There is no central control node. The devices in the network learn the reachability of the network through protocol transfer. Each device decides how to forward it. Directly led to no overall concept, can not regulate traffic from the perspective of the entire network. In order to complete the interworking between all network devices, it is necessary to use a common language. This is the network protocol. RFC is the law of the network protocol. It is equivalent to international law. Each device supplier follows the international law and basically guarantees the entire network world. normal operation. Underlay is the network of the current data center network forwarding architecture. As long as any two routes on the data center network are reachable, it refers to the physical base layer. We can improve the Underlay network through the technical improvement of the physical network equipment itself, the expansion of the number of devices, and the bandwidth scale. It includes all existing traditional network technologies.